AI is changing industries and economies worldwide.
Workforce development is central to ensuring the changes benefit all of us, as Louis Stewart, head of strategic initiatives for NVIDIA’s global developer ecosystem, explains in the latest AI Podcast.
“AI is fueling a lot of change in all ecosystems right now,” Stewart said. “It’s disrupting how we think about traditional economic development — how states and countries plan, how they stay competitive globally, and how they develop their workforces.”
Providing AI education, embracing the technology and addressing workforce challenges are all critical for future workplace development.
“It starts with education,” Stewart said.
AI Education Crucial at All Levels
Educating people on what AI can do, and how the current generation of AI-powered tools work, is the starting point. AI education must come at all levels, according to Stewart — however, higher education systems, in particular, need to be thinking about what’s coming next, so graduating students can optimize their employability.
“Graduates need to understand AI, and need to have had touches in AI,” he explained. Stewart emphasizes that this is broader than an engineering or a research challenge. “This is really a true workforce issue.”
Stewart points to Gwinnett County in Georgia as an early education example, where the community has developed a full K-16 curriculum.
“If young kids are already playing with AI on their phones, they should actually be thinking about it a little bit deeper,” he said. The idea, he explained, is for kids to move beyond simply using the tech to start seeing themselves as future creators of new technology, and being part of the broader evolution.
Nobody Gets Left Out
Beyond the classroom, a comprehensive view of AI education would expose people in the broader community to AI learning opportunities, Stewart said. His experience in the public sector informs his decidedly inclusive view on the matter.
Before joining NVIDIA four years ago, Stewart spent more than a decade working for the state of California, and then its capital city of Sacramento. He points to his time as Sacramento’s chief innovation officer to illustrate how important it is that all citizens be included in progress.
“Sacramento was trying to move into a place to be an innovation leader in the state and nationally. I knew the city because I grew up here, and I knew that there were areas of the city that would never see innovation unless it was brought to them,” he explained. “So if I was bringing autonomous cars to Sacramento, it was for the legislators, and it was for the CHP (California Highway Patrol), but it was also for the people.”
Stewart elaborated that everyone coming in touch with self-driving vehicles needed to understand their impact. There was the technology itself — how autonomous vehicles work, how to use them as a passenger and so forth.
But there were also broader questions, such as how mechanics would need new training to understand the computer systems powering autonomous cars. And how parents would need to understand self-driving vehicles from the point of view of getting their kids to and from school without having to miss work to do the driving themselves.
Just as individuals will have different needs and wants from AI systems, so too will different communities, businesses and states take different approaches when implementing AI, Stewart said.
Diverse Approaches to AI Implementation
Public-private partnerships are critical to implementing AI across the U.S. and beyond. NVIDIA is partnering with states and higher education systems across the country for AI workforce development. And the programs being put in place are just as diverse as the states themselves.
“Every state has their idea about what they want to do when it comes to AI,” Stewart explained.
Still, some common goals hold across state lines. When Stewart’s team engages a governor’s office with talk of AI to empower the workforce, create job opportunities, and improve collaboration, inclusivity and growth, he finds that state officials listen.
Stewart added that they often open up about what they’ve been working on. “We’ve been pleasantly surprised at how far along some of the states are with their AI strategies,” he said.
In August, NVIDIA announced it is working with the state of California to train 100,000 people on AI skills over the next three years. It’s an undertaking that will involve all 116 of the state’s community colleges and California’s university system. NVIDIA will also collaborate with the California human resources system to help state employees understand how AI skills may be incorporated into current and future jobs.
In Mississippi, a robust AI strategy is already in place.
The Mississippi Artificial Intelligence Network (MAIN) is one of the first statewide initiatives focused on addressing the emergence of AI and its effects on various industries’ workforces. MAIN works with educational partners that include community colleges and universities in Mississippi, all collaborating to facilitate AI education and training.
Embrace Technology, Embrace the Future
Stewart said it’s important to encourage individuals, businesses and other organizations to actively engage with AI tools and develop an understanding of how they’re benefiting the workforce landscape.
“Now is not the time to stay on the sidelines,” said Stewart.“This is the time to jump in and start understanding.”
Small businesses, for example, can start using applications like ChatGPT to see firsthand how they can transform operations. From there, Stewart suggests, a business could partner with the local school system to empower student interns to develop AI-powered tools and workflows for data analysis, marketing and other needs.
It’s a win-win: The business can transform itself with AI while playing a crucial part in developing the workforce by giving students valuable real-world experience.
It’s crucial that people get up to speed on the changes that AI is driving. And that we all participate in shaping our collective future, Stewart explained.
“Workforce development is, I think, at the crux of this next part of the conversation because the innovation and the research and everything surrounding AI is driving change so rapidly,” he said.
Hear more from NVIDIA’s Louis Stewart on workforce development opportunities in the latest AI Podcast.
]]>A team of generative AI researchers created a Swiss Army knife for sound, one that allows users to control the audio output simply using text.
While some AI models can compose a song or modify a voice, none have the dexterity of the new offering.
Called Fugatto (short for Foundational Generative Audio Transformer Opus 1), it generates or transforms any mix of music, voices and sounds described with prompts using any combination of text and audio files.
For example, it can create a music snippet based on a text prompt, remove or add instruments from an existing song, change the accent or emotion in a voice — even let people produce sounds never heard before.
“This thing is wild,” said Ido Zmishlany, a multi-platinum producer and songwriter — and cofounder of One Take Audio, a member of the NVIDIA Inception program for cutting-edge startups. “Sound is my inspiration. It’s what moves me to create music. The idea that I can create entirely new sounds on the fly in the studio is incredible.”
A Sound Grasp of Audio
“We wanted to create a model that understands and generates sound like humans do,” said Rafael Valle, a manager of applied audio research at NVIDIA and one of the dozen-plus people behind Fugatto, as well as an orchestral conductor and composer.
Supporting numerous audio generation and transformation tasks, Fugatto is the first foundational generative AI model that showcases emergent properties — capabilities that arise from the interaction of its various trained abilities — and the ability to combine free-form instructions.
“Fugatto is our first step toward a future where unsupervised multitask learning in audio synthesis and transformation emerges from data and model scale,” Valle said.
A Sample Playlist of Use Cases
For example, music producers could use Fugatto to quickly prototype or edit an idea for a song, trying out different styles, voices and instruments. They could also add effects and enhance the overall audio quality of an existing track.
“The history of music is also a history of technology. The electric guitar gave the world rock and roll. When the sampler showed up, hip-hop was born,” said Zmishlany. “With AI, we’re writing the next chapter of music. We have a new instrument, a new tool for making music — and that’s super exciting.”
An ad agency could apply Fugatto to quickly target an existing campaign for multiple regions or situations, applying different accents and emotions to voiceovers.
Language learning tools could be personalized to use any voice a speaker chooses. Imagine an online course spoken in the voice of any family member or friend.
Video game developers could use the model to modify prerecorded assets in their title to fit the changing action as users play the game. Or, they could create new assets on the fly from text instructions and optional audio inputs.
Making a Joyful Noise
“One of the model’s capabilities we’re especially proud of is what we call the avocado chair,” said Valle, referring to a novel visual created by a generative AI model for imaging.
For instance, Fugatto can make a trumpet bark or a saxophone meow. Whatever users can describe, the model can create.
With fine-tuning and small amounts of singing data, researchers found it could handle tasks it was not pretrained on, like generating a high-quality singing voice from a text prompt.
Users Get Artistic Controls
Several capabilities add to Fugatto’s novelty.
During inference, the model uses a technique called ComposableART to combine instructions that were only seen separately during training. For example, a combination of prompts could ask for text spoken with a sad feeling in a French accent.
The model’s ability to interpolate between instructions gives users fine-grained control over text instructions, in this case the heaviness of the accent or the degree of sorrow.
“I wanted to let users combine attributes in a subjective or artistic way, selecting how much emphasis they put on each one,” said Rohan Badlani, an AI researcher who designed these aspects of the model.
“In my tests, the results were often surprising and made me feel a little bit like an artist, even though I’m a computer scientist,” said Badlani, who holds a master’s degree in computer science with a focus on AI from Stanford.
The model also generates sounds that change over time, a feature he calls temporal interpolation. It can, for instance, create the sounds of a rainstorm moving through an area with crescendos of thunder that slowly fade into the distance. It also gives users fine-grained control over how the soundscape evolves.
Plus, unlike most models, which can only recreate the training data they’ve been exposed to, Fugatto allows users to create soundscapes it’s never seen before, such as a thunderstorm easing into a dawn with the sound of birds singing.
A Look Under the Hood
Fugatto is a foundational generative transformer model that builds on the team’s prior work in areas such as speech modeling, audio vocoding and audio understanding.
The full version uses 2.5 billion parameters and was trained on a bank of NVIDIA DGX systems packing 32 NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs.
Fugatto was made by a diverse group of people from around the world, including India, Brazil, China, Jordan and South Korea. Their collaboration made Fugatto’s multi-accent and multilingual capabilities stronger.
One of the hardest parts of the effort was generating a blended dataset that contains millions of audio samples used for training. The team employed a multifaceted strategy to generate data and instructions that considerably expanded the range of tasks the model could perform, while achieving more accurate performance and enabling new tasks without requiring additional data.
They also scrutinized existing datasets to reveal new relationships among the data. The overall work spanned more than a year.
Valle remembers two moments when the team knew it was on to something. “The first time it generated music from a prompt, it blew our minds,” he said.
Later, the team demoed Fugatto responding to a prompt to create electronic music with dogs barking in time to the beat.
“When the group broke up with laughter, it really warmed my heart.”
Hear what Fugatto can do:
]]>Editor’s note: This post is the first in the AI On blog series, which explores the latest techniques and real-world applications of agentic AI, chatbots and copilots. The series will also highlight the NVIDIA software and hardware powering advanced AI agents, which form the foundation of AI query engines that gather insights and perform tasks to transform everyday experiences and reshape industries.
Whether it’s getting a complex service claim resolved or having a simple purchase inquiry answered, customers expect timely, accurate responses to their requests.
AI agents can help organizations meet this need. And they can grow in scope and scale as businesses grow, helping keep customers from taking their business elsewhere.
AI agents can be used as virtual assistants, which use artificial intelligence and natural language processing to handle high volumes of customer service requests. By automating routine tasks, AI agents ease the workload on human agents, allowing them to focus on tasks requiring a more personal touch.
AI-powered customer service tools like chatbots have become table stakes across every industry looking to increase efficiency and keep buyers happy. According to a recent IDC study on conversational AI, 41% of organizations use AI-powered copilots for customer service and 60% have implemented them for IT help desks.
Now, many of those same industries are looking to adopt agentic AI, semi-autonomous tools that have the ability to perceive, reason and act on more complex problems.
How AI Agents Enhance Customer Service
A primary value of AI-powered systems is the time they free up by automating routine tasks. AI agents can perform specific tasks, or agentic operations, essentially becoming part of an organization’s workforce — working alongside humans who can focus on more complex customer issues.
AI agents can handle predictive tasks and problem-solve, can be trained to understand industry-specific terms and can pull relevant information from an organization’s knowledge bases, wherever that data resides.
With AI agents, companies can:
- Boost efficiency: AI agents handle common questions and repetitive tasks, allowing support teams to prioritize more complicated cases. This is especially useful during high-demand periods.
- Increase customer satisfaction: Faster, more personalized interactions result in happier and more loyal customers. Consistent and accurate support improves customer sentiment and experience.
- Scale Easily: Equipped to handle high volumes of customer support requests, AI agents scale effortlessly with growing businesses, reducing customer wait times and resolving issues faster.
AI Agents for Customer Service Across Industries
AI agents are transforming customer service across sectors, helping companies enhance customer conversations, achieve high-resolution rates and improve human representative productivity.
For instance, ServiceNow recently introduced IT and customer service management AI agents to boost productivity by autonomously solving many employee and customer issues. Its agents can understand context, create step-by-step resolutions and get live agent approvals when needed.
To improve patient care and reduce preprocedure anxiety, The Ottawa Hospital is using AI agents that have consistent, accurate and continuous access to information. The agent has the potential to improve patient care and reduce administrative tasks for doctors and nurses.
The city of Amarillo, Texas, uses a multilingual digital assistant named Emma to provide its residents with 24/7 support. Emma brings more effective and efficient disbursement of important information to all residents, including the one-quarter who don’t speak English.
AI agents meet current customer service demands while preparing organizations for the future.
Key Steps for Designing AI Virtual Assistants for Customer Support
AI agents for customer service come in a wide range of designs, from simple text-based virtual assistants that resolve customer issues, to animated avatars that can provide a more human-like experience.
Digital human interfaces can add warmth and personality to the customer experience. These agents respond with spoken language and even animated avatars, enhancing service interactions with a touch of real-world flair. A digital human interface lets companies customize the assistant’s appearance and tone, aligning it with the brand’s identity.
There are three key building blocks to creating an effective AI agent for customer service:
- Collect and organize customer data: AI agents need a solid base of customer data (such as profiles, past interactions, and transaction histories) to provide accurate, context-aware responses.
- Use memory functions for personalization: Advanced AI systems remember past interactions, allowing agents to deliver personalized support that feels human.
- Build an operations pipeline: Customer service teams should regularly review feedback and update the AI agent’s responses to ensure it’s always improving and aligned with business goals.
Powering AI Agents With NVIDIA NIM Microservices
NVIDIA NIM microservices power AI agents by enabling natural language processing, contextual retrieval and multilingual communication. This allows AI agents to deliver fast, personalized and accurate support tailored to diverse customer needs.
Key NVIDIA NIM microservices for customer service agents include:
NVIDIA NIM for Large Language Models — Microservices that bring advanced language models to applications and enable complex reasoning, so AI agents can understand complicated customer queries.
NVIDIA NeMo Retriever NIM — Embedding and reranking microservices that support retrieval-augmented generation pipelines allow virtual assistants to quickly access enterprise knowledge bases and boost retrieval performance by ranking relevant knowledge-base articles and improving context accuracy.
NVIDIA NIM for Digital Humans — Microservices that enable intelligent, interactive avatars to understand speech and respond in a natural way. NVIDIA Riva NIM microservices for text-to-speech, automatic speech recognition (ASR), and translation services enable AI agents to communicate naturally across languages. The recently released Riva NIM microservices for ASR enable additional multilingual enhancements. To build realistic avatars, Audio2Face NIM converts streamed audio to facial movements for real-time lip syncing. 2D and 3D Audio2Face NIM microservices support varying use cases.
Getting Started With AI Agents for Customer Service
NVIDIA AI Blueprints make it easy to start building and setting up virtual assistants by offering ready-made workflows and tools to accelerate deployment. Whether for a simple AI-powered chatbot or a fully animated digital human interface, the blueprints offer resources to create AI assistants that are scalable, aligned with an organization’s brand and deliver a responsive, efficient customer support experience.
Editor’s note: IDC figures are sourced to IDC, Market Analysis Perspective: Worldwide Conversational AI Tools and Technologies, 2024 US51619524, Sept 2024
]]>The U.S. Department of Energy oversees national energy policy and production. As big a job as that is, the DOE also does so much more — enough to have earned the nickname “Department of Everything.”
In this episode of the NVIDIA AI Podcast, Helena Fu, director of the DOE’s Office of Critical and Emerging Technologies (CET) and DOE’s chief AI officer, talks about the department’s latest AI efforts. With initiatives touching national security, infrastructure and utilities, and oversight of 17 national labs and 34 scientific user facilities dedicated to scientific discovery and industry innovation, DOE and CET are central to AI-related research and development throughout the country.
Hear more from Helena Fu by watching the on-demand session, AI for Science, Energy and Security, from AI Summit DC. And learn more about software-defined infrastructure for power and utilities.
Time Stamps
2:20: Four areas of focus for the CET include AI, microelectronics, quantum information science and biotechnology.
10:55: Introducing AI-related initiatives within the DOE, including FASST, or Frontiers in AI for Science, Security and Technology.
16:30: Discussing future applications of AI, large language models and more.
19:35: The opportunity of AI applied to materials discovery and applications across science, energy and national security.
You Might Also Like…
NVIDIA’s Josh Parker on How AI and Accelerated Computing Drive Sustainability – Ep. 234
AI isn’t just about building smarter machines. It’s about building a greener world. AI and accelerated computing are helping industries tackle some of the world’s toughest environmental challenges. Joshua Parker, senior director of corporate sustainability at NVIDIA, explains how these technologies are powering a new era of energy efficiency.
Currents of Change: ITIF’s Daniel Castro on Energy-Efficient AI and Climate Change
AI is everywhere. So, too, are concerns about advanced technology’s environmental impact. Daniel Castro, vice president of the Information Technology and Innovation Foundation and director of its Center for Data Innovation, discusses his AI energy use report that addresses misconceptions about AI’s energy consumption. He also talks about the need for continued development of energy-efficient technology.
How the Ohio Supercomputer Center Drives the Future of Computing – Ep. 213
The Ohio Supercomputer Center’s Open OnDemand program empowers the state’s educational institutions and industries with computational services, training and educational programs. They’ve even helped NASCAR simulate race car designs. Alan Chalker, the director of strategic programs at the OSC, talks about all things supercomputing.
Anima Anandkumar on Using Generative AI to Tackle Global Challenges – Ep. 204
Anima Anandkumar, Bren Professor at Caltech and former senior director of AI research at NVIDIA, speaks to generative AI’s potential to make splashes in the scientific community, from accelerating drug and vaccine research to predicting extreme weather events like hurricanes or heat waves.
Subscribe to the AI Podcast
Get the AI Podcast through iTunes, Google Play, Amazon Music, Castbox, DoggCatcher, Overcast, PlayerFM, Pocket Casts, Podbay, PodBean, PodCruncher, PodKicker, Soundcloud, Spotify, Stitcher and TuneIn.
Make the AI Podcast better: Have a few minutes to spare? Fill out this listener survey.
]]>Generative AI-powered laptops and PCs are unlocking advancements in gaming, content creation, productivity and development. Today, over 600 Windows apps and games are already running AI locally on more than 100 million GeForce RTX AI PCs worldwide, delivering fast, reliable and low-latency performance.
At Microsoft Ignite, NVIDIA and Microsoft announced tools to help Windows developers quickly build and optimize AI-powered apps on RTX AI PCs, making local AI more accessible. These new tools enable application and game developers to harness powerful RTX GPUs to accelerate complex AI workflows for applications such as AI agents, app assistants and digital humans.
RTX AI PCs Power Digital Humans With Multimodal Small Language Models

NVIDIA ACE is a suite of digital human technologies that brings life to agents, assistants and avatars. To achieve a higher level of understanding so that they can respond with greater context-awareness, digital humans must be able to visually perceive the world like humans do.
Enhancing digital human interactions with greater realism demands technology that enables perception and understanding of their surroundings with greater nuance. To achieve this, NVIDIA developed multimodal small language models that can process both text and imagery, excel in role-playing and are optimized for rapid response times.
The NVIDIA Nemovision-4B-Instruct model, soon to be available, uses the latest NVIDIA VILA and NVIDIA NeMo framework for distilling, pruning and quantizing to become small enough to perform on RTX GPUs with the accuracy developers need.
The model enables digital humans to understand visual imagery in the real world and on the screen to deliver relevant responses. Multimodality serves as the foundation for agentic workflows and offers a sneak peek into a future where digital humans can reason and take action with minimal assistance from a user.
NVIDIA is also introducing the Mistral NeMo Minitron 128k Instruct family, a suite of large-context small language models designed for optimized, efficient digital human interactions, coming soon. Available in 8B-, 4B- and 2B-parameter versions, these models offer flexible options for balancing speed, memory usage and accuracy on RTX AI PCs. They can handle large datasets in a single pass, eliminating the need for data segmentation and reassembly. Built in the GGUF format, these models enhance efficiency on low-power devices and support compatibility with multiple programming languages.
Turbocharge Gen AI With NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer for Windows
When bringing models to PC environments, developers face the challenge of limited memory and compute resources for running AI locally. And they want to make models available to as many people as possible, with minimal accuracy loss.
Today, NVIDIA announced updates to NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer (ModelOpt) to offer Windows developers an improved way to optimize models for ONNX Runtime deployment.
With the latest updates, TensorRT ModelOpt enables models to be optimized into an ONNX checkpoint for deploying the model within ONNX runtime environments — using GPU execution providers such as CUDA, TensorRT and DirectML.
TensorRT-ModelOpt includes advanced quantization algorithms, such as INT4-Activation Aware Weight Quantization. Compared to other tools such as Olive, the new method reduces the memory footprint of the model and improves throughput performance on RTX GPUs.
During deployment, the models can have up to 2.6x reduced memory footprint compared to FP16 models. This results in faster throughput, with minimal accuracy degradation, allowing them to run on a wider range of PCs.
Learn more about how developers on Microsoft systems, from Windows RTX AI PCs to NVIDIA Blackwell-powered Azure servers, are transforming how users interact with AI on a daily basis.
]]>Editor’s note: This article, originally published on November 15, 2023, has been updated.
To understand the latest advance in generative AI, imagine a courtroom.
Judges hear and decide cases based on their general understanding of the law. Sometimes a case — like a malpractice suit or a labor dispute — requires special expertise, so judges send court clerks to a law library, looking for precedents and specific cases they can cite.
Like a good judge, large language models (LLMs) can respond to a wide variety of human queries. But to deliver authoritative answers that cite sources, the model needs an assistant to do some research.
The court clerk of AI is a process called retrieval-augmented generation, or RAG for short.
How It Got Named ‘RAG’
Patrick Lewis, lead author of the 2020 paper that coined the term, apologized for the unflattering acronym that now describes a growing family of methods across hundreds of papers and dozens of commercial services he believes represent the future of generative AI.

“We definitely would have put more thought into the name had we known our work would become so widespread,” Lewis said in an interview from Singapore, where he was sharing his ideas with a regional conference of database developers.
“We always planned to have a nicer sounding name, but when it came time to write the paper, no one had a better idea,” said Lewis, who now leads a RAG team at AI startup Cohere.
So, What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is a technique for enhancing the accuracy and reliability of generative AI models with facts fetched from external sources.
In other words, it fills a gap in how LLMs work. Under the hood, LLMs are neural networks, typically measured by how many parameters they contain. An LLM’s parameters essentially represent the general patterns of how humans use words to form sentences.
That deep understanding, sometimes called parameterized knowledge, makes LLMs useful in responding to general prompts at light speed. However, it does not serve users who want a deeper dive into a current or more specific topic.
Combining Internal, External Resources
Lewis and colleagues developed retrieval-augmented generation to link generative AI services to external resources, especially ones rich in the latest technical details.
The paper, with coauthors from the former Facebook AI Research (now Meta AI), University College London and New York University, called RAG “a general-purpose fine-tuning recipe” because it can be used by nearly any LLM to connect with practically any external resource.
Building User Trust
Retrieval-augmented generation gives models sources they can cite, like footnotes in a research paper, so users can check any claims. That builds trust.
What’s more, the technique can help models clear up ambiguity in a user query. It also reduces the possibility a model will make a wrong guess, a phenomenon sometimes called hallucination.
Another great advantage of RAG is it’s relatively easy. A blog by Lewis and three of the paper’s coauthors said developers can implement the process with as few as five lines of code.
That makes the method faster and less expensive than retraining a model with additional datasets. And it lets users hot-swap new sources on the fly.
How People Are Using RAG
With retrieval-augmented generation, users can essentially have conversations with data repositories, opening up new kinds of experiences. This means the applications for RAG could be multiple times the number of available datasets.
For example, a generative AI model supplemented with a medical index could be a great assistant for a doctor or nurse. Financial analysts would benefit from an assistant linked to market data.
In fact, almost any business can turn its technical or policy manuals, videos or logs into resources called knowledge bases that can enhance LLMs. These sources can enable use cases such as customer or field support, employee training and developer productivity.
The broad potential is why companies including AWS, IBM, Glean, Google, Microsoft, NVIDIA, Oracle and Pinecone are adopting RAG.
Getting Started With Retrieval-Augmented Generation
To help users get started, NVIDIA developed an AI Blueprint for building virtual assistants. Organizations can use this reference architecture to quickly scale their customer service operations with generative AI and RAG, or get started building a new customer-centric solution.
The blueprint uses some of the latest AI-building methodologies and NVIDIA NeMo Retriever, a collection of easy-to-use NVIDIA NIM microservices for large-scale information retrieval. NIM eases the deployment of secure, high-performance AI model inferencing across clouds, data centers and workstations.
These components are all part of NVIDIA AI Enterprise, a software platform that accelerates the development and deployment of production-ready AI with the security, support and stability businesses need.
There is also a free hands-on NVIDIA LaunchPad lab for developing AI chatbots using RAG so developers and IT teams can quickly and accurately generate responses based on enterprise data.
Getting the best performance for RAG workflows requires massive amounts of memory and compute to move and process data. The NVIDIA GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip, with its 288GB of fast HBM3e memory and 8 petaflops of compute, is ideal — it can deliver a 150x speedup over using a CPU.
Once companies get familiar with RAG, they can combine a variety of off-the-shelf or custom LLMs with internal or external knowledge bases to create a wide range of assistants that help their employees and customers.
RAG doesn’t require a data center. LLMs are debuting on Windows PCs, thanks to NVIDIA software that enables all sorts of applications users can access even on their laptops.
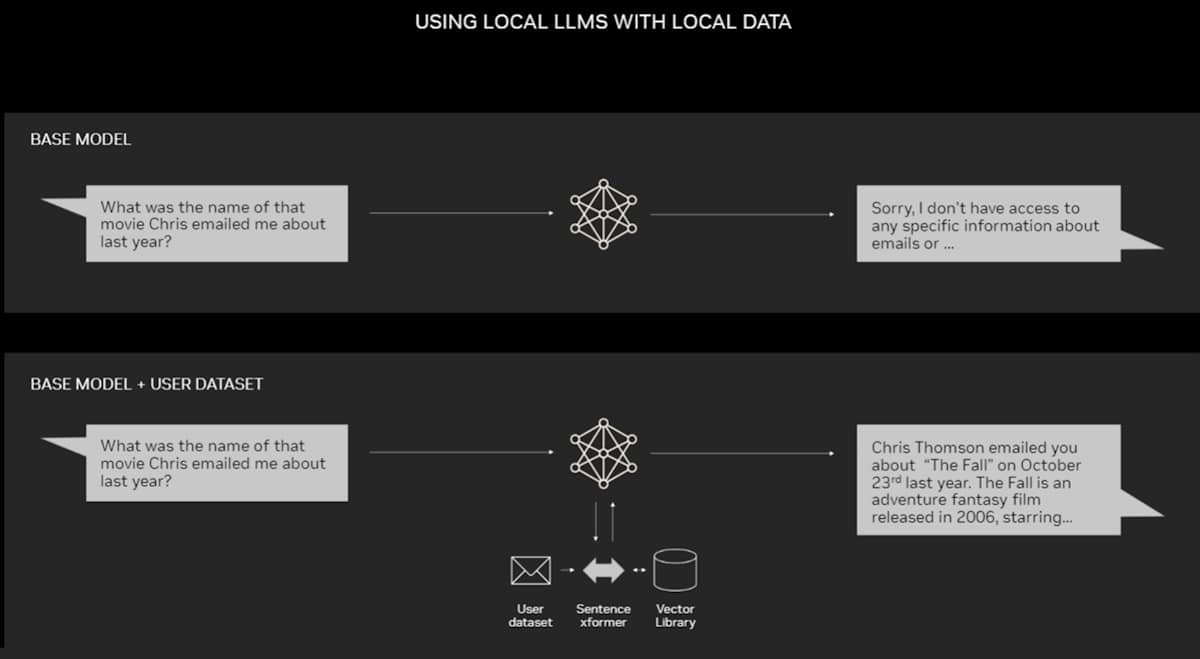
PCs equipped with NVIDIA RTX GPUs can now run some AI models locally. By using RAG on a PC, users can link to a private knowledge source – whether that be emails, notes or articles – to improve responses. The user can then feel confident that their data source, prompts and response all remain private and secure.
A recent blog provides an example of RAG accelerated by TensorRT-LLM for Windows to get better results fast.
The History of RAG
The roots of the technique go back at least to the early 1970s. That’s when researchers in information retrieval prototyped what they called question-answering systems, apps that use natural language processing (NLP) to access text, initially in narrow topics such as baseball.
The concepts behind this kind of text mining have remained fairly constant over the years. But the machine learning engines driving them have grown significantly, increasing their usefulness and popularity.
In the mid-1990s, the Ask Jeeves service, now Ask.com, popularized question answering with its mascot of a well-dressed valet. IBM’s Watson became a TV celebrity in 2011 when it handily beat two human champions on the Jeopardy! game show.
Today, LLMs are taking question-answering systems to a whole new level.
Insights From a London Lab
The seminal 2020 paper arrived as Lewis was pursuing a doctorate in NLP at University College London and working for Meta at a new London AI lab. The team was searching for ways to pack more knowledge into an LLM’s parameters and using a benchmark it developed to measure its progress.
Building on earlier methods and inspired by a paper from Google researchers, the group “had this compelling vision of a trained system that had a retrieval index in the middle of it, so it could learn and generate any text output you wanted,” Lewis recalled.

When Lewis plugged into the work in progress a promising retrieval system from another Meta team, the first results were unexpectedly impressive.
“I showed my supervisor and he said, ‘Whoa, take the win. This sort of thing doesn’t happen very often,’ because these workflows can be hard to set up correctly the first time,” he said.
Lewis also credits major contributions from team members Ethan Perez and Douwe Kiela, then of New York University and Facebook AI Research, respectively.
When complete, the work, which ran on a cluster of NVIDIA GPUs, showed how to make generative AI models more authoritative and trustworthy. It’s since been cited by hundreds of papers that amplified and extended the concepts in what continues to be an active area of research.
How Retrieval-Augmented Generation Works
At a high level, here’s how an NVIDIA technical brief describes the RAG process.
When users ask an LLM a question, the AI model sends the query to another model that converts it into a numeric format so machines can read it. The numeric version of the query is sometimes called an embedding or a vector.
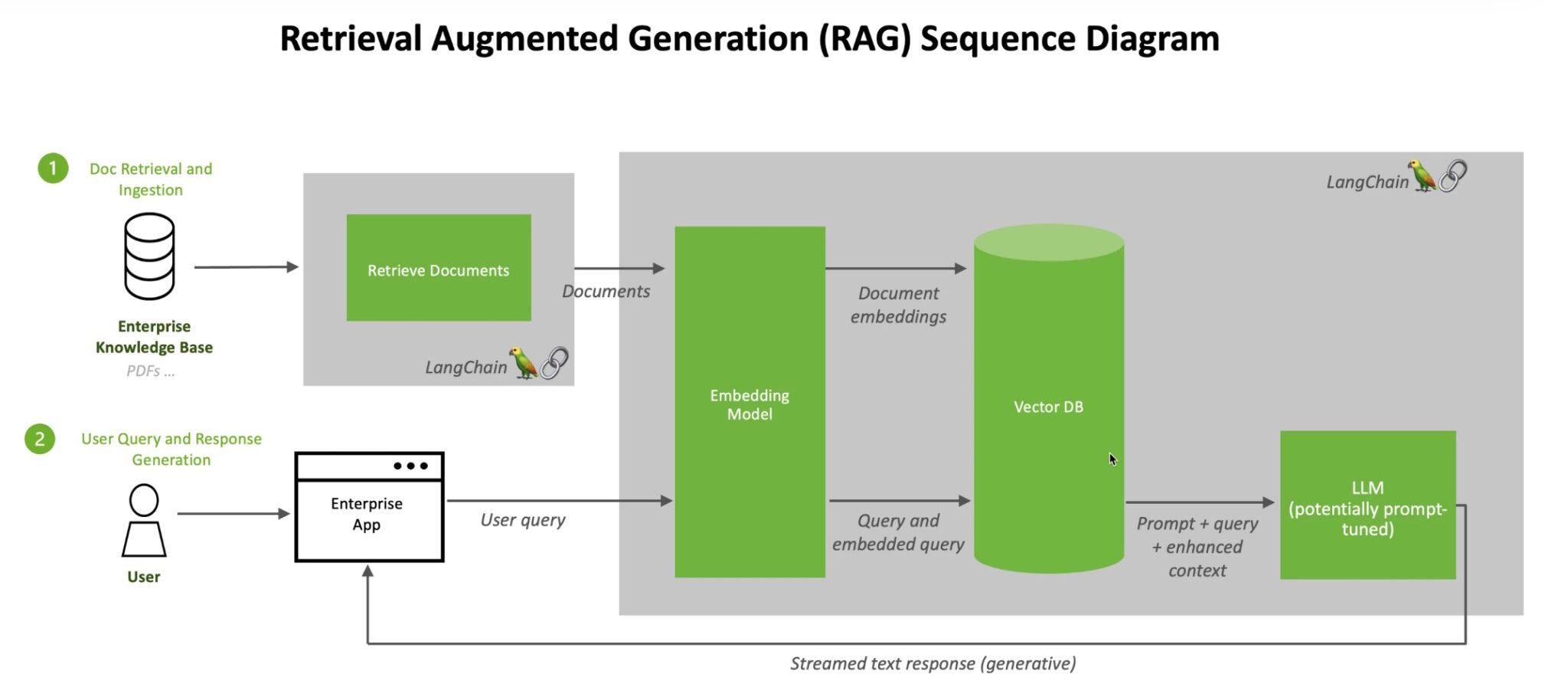
The embedding model then compares these numeric values to vectors in a machine-readable index of an available knowledge base. When it finds a match or multiple matches, it retrieves the related data, converts it to human-readable words and passes it back to the LLM.
Finally, the LLM combines the retrieved words and its own response to the query into a final answer it presents to the user, potentially citing sources the embedding model found.
Keeping Sources Current
In the background, the embedding model continuously creates and updates machine-readable indices, sometimes called vector databases, for new and updated knowledge bases as they become available.
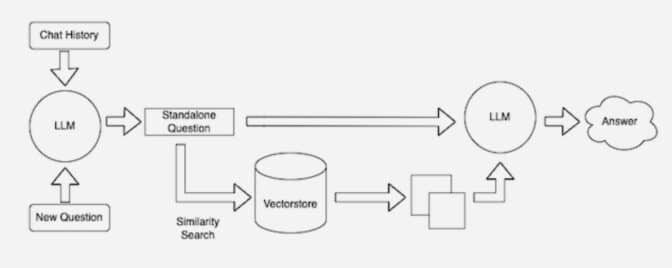
Many developers find LangChain, an open-source library, can be particularly useful in chaining together LLMs, embedding models and knowledge bases. NVIDIA uses LangChain in its reference architecture for retrieval-augmented generation.
The LangChain community provides its own description of a RAG process.
Looking forward, the future of generative AI lies in creatively chaining all sorts of LLMs and knowledge bases together to create new kinds of assistants that deliver authoritative results users can verify.
Explore generative AI sessions and experiences at NVIDIA GTC, the global conference on AI and accelerated computing, running March 18-21 in San Jose, Calif., and online.
]]>Diabetics — or others monitoring their sugar intake — may look at a cookie and wonder, “How will eating this affect my glucose levels?” A generative AI model can now predict the answer.
Researchers from the Weizmann Institute of Science, Tel Aviv-based startup Pheno.AI and NVIDIA led the development of GluFormer, an AI model that can predict an individual’s future glucose levels and other health metrics based on past glucose monitoring data.
Data from continuous glucose monitoring could help more quickly diagnose patients with prediabetes or diabetes, according to Harvard Health Publishing and NYU Langone Health. GluFormer’s AI capabilities can further enhance the value of this data, helping clinicians and patients spot anomalies, predict clinical trial outcomes and forecast health outcomes up to four years in advance.
The researchers showed that, after adding dietary intake data into the model, GluFormer can also predict how a person’s glucose levels will respond to specific foods and dietary changes, enabling precision nutrition.
Accurate predictions of glucose levels for those at high risk of developing diabetes could enable doctors and patients to adopt preventative care strategies sooner, improving patient outcomes and reducing the economic impact of diabetes, which could reach $2.5 trillion globally by 2030.
AI tools like GluFormer have the potential to help the hundreds of millions of adults with diabetes. The condition currently affects around 10% of the world’s adults — a figure that could potentially double by 2050 to impact over 1.3 billion people. It’s one of the 10 leading causes of death globally, with side effects including kidney damage, vision loss and heart problems.
GluFormer is a transformer model, a kind of neural network architecture that tracks relationships in sequential data. It’s the same architecture as OpenAI’s GPT models — in this case generating glucose levels instead of text.
“Medical data, and continuous glucose monitoring in particular, can be viewed as sequences of diagnostic tests that trace biological processes throughout life,” said Gal Chechik, senior director of AI research at NVIDIA. “We found that the transformer architecture, developed for long text sequences, can take a sequence of medical tests and predict the results of the next test. In doing so, it learns something about how the diagnostic measurements develop over time.”
The model was trained on 14 days of glucose monitoring data from over 10,000 non-diabetic study participants, with data collected every 15 minutes through a wearable monitoring device. The data was collected as part of the Human Phenotype Project, an initiative by Pheno.AI, a startup that aims to improve human health through data collection and analysis.
“Two important factors converged at the same time to enable this research: the maturing of generative AI technology powered by NVIDIA and the collection of large-scale health data by the Weizmann Institute,” said the paper’s lead author, Guy Lutsker, an NVIDIA researcher and Ph.D. student at the Weizmann Institute of Science. “It put us in the unique position to extract interesting medical insights from the data.”
The research team validated GluFormer across 15 other datasets and found it generalizes well to predict health outcomes for other groups, including those with prediabetes, type 1 and type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes and obesity.
They used a cluster of NVIDIA Tensor Core GPUs to accelerate model training and inference.
Beyond glucose levels, GluFormer can predict medical values including visceral adipose tissue, a measure of the amount of body fat around organs like the liver and pancreas; systolic blood pressure, which is associated with diabetes risk; and apnea-hypopnea index, a measurement for sleep apnea, which is linked to type 2 diabetes.
Read the GluFormer research paper on Arxiv.
]]>Working with NVIDIA and its partners, Indonesia’s technology leaders have launched an initiative to bring sovereign AI to the nation’s more than 277 million Indonesian speakers.
The collaboration is grounded in a broad public-private partnership that reflects the nation’s concept of “gotong royong,” a term describing a spirit of mutual assistance and community collaboration.
NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang joined Indonesia Minster for State-Owned Enterprises Erick Thohir, Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison (IOH) President Director and CEO Vikram Sinha, GoTo CEO Patrick Walujo and other leaders in Jakarta to celebrate the launch of Sahabat-AI.
Sahabat-AI is a collection of open-source Indonesian large language models (LLMs) that local industries, government agencies, universities and research centers can use to create generative AI applications. Built with NVIDIA NeMo and NVIDIA NIM microservices, the models were launched today at Indonesia AI Day, a conference focused on enabling AI sovereignty and driving AI-driven digital independence in the country.
Built by Indonesians, for Indonesians, Sahabat-AI models understand local contexts and enable people to build generative AI services and applications in Bahasa Indonesian and various local languages. The models form the foundation of a collaborative effort to empower Indonesia through a locally developed, open-source LLM ecosystem.
“Artificial intelligence will democratize technology. It is the great equalizer,” said Huang. “The technology is complicated but the benefit is not.”
“Sahabat-AI is not just a technological achievement, it embodies Indonesia’s vision for a future where digital sovereignty and inclusivity go hand in hand,” Sinha said. “By creating an AI model that speaks our language and reflects our culture, we’re empowering every Indonesian to harness advanced technology’s potential. This initiative is a crucial step toward democratizing AI as a tool for growth, innovation and empowerment across our diverse society.”
To accelerate this initiative, IOH — one of Indonesia’s largest telecom and internet companies — earlier this year launched “GPU Merdeka by Lintasarta,” an NVIDIA-accelerated sovereign AI cloud. The GPU Merdeka cloud service operates at a BDx Indonesia AI data center powered by renewable energy.
Bolstered by the NVIDIA Cloud Partner program, IOH subsidiary Lintasarta built the high-performance AI cloud in less than three months, a feat that would’ve taken much longer without NVIDIA’s technology infrastructure. The AI cloud is now driving transformation across energy, financial services, healthcare and other industries.
The NVIDIA Cloud Partner (NCP) program provides Lintasarta with access to NVIDIA reference architectures — blueprints for building high-performance, scalable and secure data centers.
The program also offers technological and go-to-market support, access to the latest NVIDIA AI software and accelerated computing platforms, and opportunities to collaborate with NVIDIA’s extensive ecosystem of industry partners. These partners include global systems integrators like Accenture and Tech Mahindra and software companies like GoTo and Hippocratic AI, each of which is working alongside IOH to boost the telco’s sovereign AI initiatives.
Developing Industry-Specific Applications With Accenture
Partnering with leading professional services company Accenture, IOH is developing applications for industry-specific use cases based on its new AI cloud, Sahabat-AI and the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform.
NVIDIA CEO Huang joined Accenture CEO Julie Sweet in a fireside chat during Indonesia AI Day to discuss how the companies are supporting enterprise and industrial AI in Indonesia.
The collaboration taps into the Accenture AI Refinery platform to help Indonesian enterprises build AI solutions tailored for financial services, energy and other industries, while delivering sovereign data governance.
Initially focused on financial services, IOH’s work with Accenture and NVIDIA technologies is delivering pre-built enterprise solutions that can help Indonesian banks more quickly harness AI.
With a modular architecture, these solutions can meet clients’ needs wherever they are in their AI journeys, helping increase profitability, operational efficiency and sustainable growth.
Building the Indonesian LLM and Chatbot Services With Tech Mahindra
Built with India-based global systems integrator Tech Mahindra, the Sahabat-AI LLMs power various AI services in Indonesia.
For example, Sahabat-AI enables IOH’s AI chatbot to answer queries in the Indonesian language for various citizen and resident services. A person could ask about processes for updating their national identification card, as well as about tax rates, payment procedures, deductions and more.
The chatbot integrates with a broader citizen services platform Tech Mahindra and IOH are developing as part of the Indonesian government’s sovereign AI initiative.
Indosat developed Sahabat-AI using the NVIDIA NeMo platform for developing customized LLMs. The team fine-tuned a version of the Llama 3 8B model, customizing it for Bahasa Indonesian using a diverse dataset tailored for effective communication with users.
To further optimize performance, Sahabat-AI uses NVIDIA NIM microservices, which have demonstrated up to 2.5x greater throughput compared with standard implementations. This improvement in processing efficiency allows for faster responses and more satisfying user experiences.
In addition, NVIDIA NeMo Guardrails open-source software orchestrates dialog management and helps ensure accuracy, appropriateness and security of the LLM-based chatbot.
Many other service capabilities tapping Sahabat-AI are also planned for development, including AI-powered healthcare services and other local applications.
Improving Indonesian Healthcare With Hippocratic AI
Among the first to tap into Sahabat-AI is healthcare AI company Hippocratic AI, which is using the models, the NVIDIA AI platform and IOH’s sovereign AI cloud to develop digital agents that can have humanlike conversations, exhibit empathic qualities, and build rapport and trust with patients across Indonesia.
Hippocratic AI empowers a novel trillion-parameter constellation architecture that brings together specialized healthcare LLM agents to deliver safe, accurate digital agent implementation.
Digital AI agents can significantly increase staff productivity by offloading time-consuming tasks, allowing human nurses and medical professionals to focus on critical duties to increase healthcare accessibility and quality of service.
IOH’s sovereign AI cloud lets Hippocratic AI keep patient data local and secure, and enables extremely low-latency AI inference for its LLMs.
Enhancing Simplicity, Accessibility for On-Demand and Financial Services With GoTo
GoTo offers technology infrastructure and solutions that help users thrive in the digital economy, including through applications spanning on-demand services for transport, food, grocery and logistics delivery, financial services and e-commerce.
The company — which operates one of Indonesia’s leading on-demand transport services, as well as a leading payment application in the country — is adopting and enhancing the new Sahabat-AI models to integrate with its AI voice assistant, called Dira.
Dira is a speech and generative AI-powered digital assistant that helps customers book rides, order food deliveries, transfer money, pay bills and more.
Tapping into Sahabat-AI, Dira is poised to deliver more localized and culturally relevant interactions with application users.
Advancing Sustainability Within Lintasarta as IOH’s AI Factory
Fundamentally, Lintasarta’s AI cloud is an AI factory — a next-generation data center that hosts advanced, full-stack accelerated computing platforms for the most computationally intensive tasks. It’ll enable regional governments, businesses and startups to build, customize and deploy generative AI applications aligned with local language and customs.
Looking forward, Lintasarta plans to expand its AI factory with the most advanced NVIDIA technologies. The infrastructure already boasts a “green” design, powered by renewable energy and sustainable technologies. Lintasarta is committed to adding value to Indonesia’s digital ecosystem with integrated, secure and sustainable technology, in line with the Golden Indonesia 2045 vision.
Beyond Indonesia, NVIDIA NIM microservices are bolstering sovereign AI models that support local languages in India, Japan, Taiwan and many other countries and regions.
NVIDIA NIM microservices, NeMo and NeMo Guardrails are available as part of the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform.
Learn more about NVIDIA-powered sovereign AI factories for telecommunications.
See notice regarding software product information.
]]>Since the advent of the computer age, industries have been so awash in stored data that most of it never gets put to use.
This data is estimated to be in the neighborhood of 120 zettabytes — the equivalent of trillions of terabytes, or more than 120x the amount of every grain of sand on every beach around the globe. Now, the world’s industries are putting that untamed data to work by building and customizing large language models (LLMs).
As 2025 approaches, industries such as healthcare, telecommunications, entertainment, energy, robotics, automotive and retail are using those models, combining it with their proprietary data and gearing up to create AI that can reason.
The NVIDIA experts below focus on some of the industries that deliver $88 trillion worth of goods and services globally each year. They predict that AI that can harness data at the edge and deliver near-instantaneous insights is coming to hospitals, factories, customer service centers, cars and mobile devices near you.
But first, let’s hear AI’s predictions for AI. When asked, “What will be the top trends in AI in 2025 for industries?” both Perplexity and ChatGPT 4.0 responded that agentic AI sits atop the list alongside edge AI, AI cybersecurity and AI-driven robots.
Agentic AI is a new category of generative AI that operates virtually autonomously. It can make complex decisions and take actions based on continuous learning and analysis of vast datasets. Agentic AI is adaptable, has defined goals and can correct itself, and can chat with other AI agents or reach out to a human for help.
Now, hear from NVIDIA experts on what to expect in the year ahead:

Kimberly Powell
Vice President of Healthcare
Human-robotic interaction: Robots will assist human clinicians in a variety of ways, from understanding and responding to human commands, to performing and assisting in complex surgeries.
It’s being made possible by digital twins, simulation and AI that train and test robotic systems in virtual environments to reduce risks associated with real-world trials. It also can train robots to react in virtually any scenario, enhancing their adaptability and performance across different clinical situations.
New virtual worlds for training robots to perform complex tasks will make autonomous surgical robots a reality. These surgical robots will perform complex surgical tasks with precision, reducing patient recovery times and decreasing the cognitive workload for surgeons.
Digital health agents: The dawn of agentic AI and multi-agent systems will address the existential challenges of workforce shortages and the rising cost of care.
Administrative health services will become digital humans taking notes for you or making your next appointment — introducing an era of services delivered by software and birthing a service-as-a-software industry.
Patient experience will be transformed with always-on, personalized care services while healthcare staff will collaborate with agents that help them reduce clerical work, retrieve and summarize patient histories, and recommend clinical trials and state-of-the-art treatments for their patients.
Drug discovery and design AI factories: Just as ChatGPT can generate an email or a poem without putting a pen to paper for trial and error, generative AI models in drug discovery can liberate scientific thinking and exploration.
Techbio and biopharma companies have begun combining models that generate, predict and optimize molecules to explore the near-infinite possible target drug combinations before going into time-consuming and expensive wet lab experiments.
The drug discovery and design AI factories will consume all wet lab data, refine AI models and redeploy those models — improving each experiment by learning from the previous one. These AI factories will shift the industry from a discovery process to a design and engineering one.
 Rev Lebaredian
Rev Lebaredian
Vice President of Omniverse and Simulation Technology
Let’s get physical (AI, that is): Getting ready for AI models that can perceive, understand and interact with the physical world is one challenge enterprises will race to tackle.
While LLMs require reinforcement learning largely in the form of human feedback, physical AI needs to learn in a “world model” that mimics the laws of physics. Large-scale physically based simulations are allowing the world to realize the value of physical AI through robots by accelerating the training of physical AI models and enabling continuous training in robotic systems across every industry.
Cheaper by the dozen: In addition to their smarts (or lack thereof), one big factor that has slowed adoption of humanoid robots has been affordability. As agentic AI brings new intelligence to robots, though, volume will pick up and costs will come down sharply. The average cost of industrial robots is expected to drop to $10,800 in 2025, down sharply from $46K in 2010 to $27K in 2017. As these devices become significantly cheaper, they’ll become as commonplace across industries as mobile devices are.
 Deepu Talla
Deepu Talla
Vice President of Robotics and Edge Computing
Redefining robots: When people think of robots today, they’re usually images or content showing autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), manipulator arms or humanoids. But tomorrow’s robots are set to be an autonomous system that perceives, reasons, plans and acts — then learns.
Soon we’ll be thinking of robots embodied everywhere from surgical rooms and data centers to warehouses and factories. Even traffic control systems or entire cities will be transformed from static, manually operated systems to autonomous, interactive systems embodied by physical AI.
The rise of small language models: To improve the functionality of robots operating at the edge, expect to see the rise of small language models that are energy-efficient and avoid latency issues associated with sending data to data centers. The shift to small language models in edge computing will improve inference in a range of industries, including automotive, retail and advanced robotics.
 Kevin Levitt
Kevin Levitt
Global Director of Financial Services
AI agents boost firm operations: AI-powered agents will be deeply integrated into the financial services ecosystem, improving customer experiences, driving productivity and reducing operational costs.
AI agents will take every form based on each financial services firm’s needs. Human-like 3D avatars will take requests and interact directly with clients, while text-based chatbots will summarize thousands of pages of data and documents in seconds to deliver accurate, tailored insights to employees across all business functions.
AI factories become table stakes: AI use cases in the industry are exploding. This includes improving identity verification for anti-money laundering and know-your-customer regulations, reducing false positives for transaction fraud and generating new trading strategies to improve market returns. AI also is automating document management, reducing funding cycles to help consumers and businesses on their financial journeys.
To capitalize on opportunities like these, financial institutions will build AI factories that use full-stack accelerated computing to maximize performance and utilization to build AI-enabled applications that serve hundreds, if not thousands, of use cases — helping set themselves apart from the competition.
AI-assisted data governance: Due to the sensitive nature of financial data and stringent regulatory requirements, governance will be a priority for firms as they use data to create reliable and legal AI applications, including for fraud detection, predictions and forecasting, real-time calculations and customer service.
Firms will use AI models to assist in the structure, control, orchestration, processing and utilization of financial data, making the process of complying with regulations and safeguarding customer privacy smoother and less labor intensive. AI will be the key to making sense of and deriving actionable insights from the industry’s stockpile of underutilized, unstructured data.
 Richard Kerris
Richard Kerris
Vice President of Media and Entertainment
Let AI entertain you: AI will continue to revolutionize entertainment with hyperpersonalized content on every screen, from TV shows to live sports. Using generative AI and advanced vision-language models, platforms will offer immersive experiences tailored to individual tastes, interests and moods. Imagine teaser images and sizzle reels crafted to capture the essence of a new show or live event and create an instant personal connection.
In live sports, AI will enhance accessibility and cultural relevance, providing language dubbing, tailored commentary and local adaptations. AI will also elevate binge-watching by adjusting pacing, quality and engagement options in real time to keep fans captivated. This new level of interaction will transform streaming from a passive experience into an engaging journey that brings people closer to the action and each other.
AI-driven platforms will also foster meaningful connections with audiences by tailoring recommendations, trailers and content to individual preferences. AI’s hyperpersonalization will allow viewers to discover hidden gems, reconnect with old favorites and feel seen. For the industry, AI will drive growth and innovation, introducing new business models and enabling global content strategies that celebrate unique viewer preferences, making entertainment feel boundless, engaging and personally crafted.
 Ronnie Vasishta
Ronnie Vasishta
Senior Vice President of Telecoms
The AI connection: Telecommunications providers will begin to deliver generative AI applications and 5G connectivity over the same network. AI radio access network (AI-RAN) will enable telecom operators to transform traditional single-purpose base stations from cost centers into revenue-producing assets capable of providing AI inference services to devices, while more efficiently delivering the best network performance.
AI agents to the rescue: The telecommunications industry will be among the first to dial into agentic AI to perform key business functions. Telco operators will use AI agents for a wide variety of tasks, from suggesting money-saving plans to customers and troubleshooting network connectivity, to answering billing questions and processing payments.
More efficient, higher-performing networks: AI also will be used at the wireless network layer to enhance efficiency, deliver site-specific learning and reduce power consumption. Using AI as an intelligent performance improvement tool, operators will be able to continuously observe network traffic, predict congestion patterns and make adjustments before failures happen, allowing for optimal network performance.
Answering the call on sovereign AI: Nations will increasingly turn to telcos — which have proven experience managing complex, distributed technology networks — to achieve their sovereign AI objectives. The trend will spread quickly across Europe and Asia, where telcos in Switzerland, Japan, Indonesia and Norway are already partnering with national leaders to build AI factories that can use proprietary, local data to help researchers, startups, businesses and government agencies create AI applications and services.
 Xinzhou Wu
Xinzhou Wu
Vice President of Automotive
Pedal to generative AI metal: Autonomous vehicles will become more performant as developers tap into advancements in generative AI. For example, harnessing foundation models, such as vision language models, provides an opportunity to use internet-scale knowledge to solve one of the hardest problems in the autonomous vehicle (AV) field, namely that of efficiently and safely reasoning through rare corner cases.
Simulation unlocks success: More broadly, new AI-based tools will enable breakthroughs in how AV development is carried out. For example, advances in generative simulation will enable the scalable creation of complex scenarios aimed at stress-testing vehicles for safety purposes. Aside from allowing for testing unusual or dangerous conditions, simulation is also essential for generating synthetic data to enable end-to-end model training.
Three-computer approach: Effectively, new advances in AI will catalyze AV software development across the three key computers underpinning AV development — one for training the AI-based stack in the data center, another for simulation and validation, and a third in-vehicle computer to process real-time sensor data for safe driving. Together, these systems will enable continuous improvement of AV software for enhanced safety and performance of cars, trucks, robotaxis and beyond.
 Marc Spieler
Marc Spieler
Senior Managing Director of Global Energy Industry
Welcoming the smart grid: Do you know when your daily peak home electricity is? You will soon as utilities around the world embrace smart meters that use AI to broadly manage their grid networks, from big power plants and substations and, now, into the home.
As the smart grid takes shape, smart meters — once deemed too expensive to be installed in millions of homes — that combine software, sensors and accelerated computing will alert utilities when trees in a backyard brush up against power lines or when to offer big rebates to buy back the excess power stored through rooftop solar installations.
Powering up: Delivering the optimal power stack has always been mission-critical for the energy industry. In the era of generative AI, utilities will address this issue in ways that reduce environmental impact.
Expect in 2025 to see a broader embrace of nuclear power as one clean-energy path the industry will take. Demand for natural gas also will grow as it replaces coal and other forms of energy. These resurgent forms of energy are being helped by the increased use of accelerated computing, simulation technology and AI and 3D visualization, which helps optimize design, pipeline flows and storage. We’ll see the same happening at oil and gas companies, which are looking to reduce the impact of energy exploration and production.
 Azita Martin
Azita Martin
Vice President of Retail, Consumer-Packaged Goods and Quick-Service Restaurants
Software-defined retail: Supercenters and grocery stores will become software-defined, each running computer vision and sophisticated AI algorithms at the edge. The transition will accelerate checkout, optimize merchandising and reduce shrink — the industry term for a product being lost or stolen.
Each store will be connected to a headquarters AI network, using collective data to become a perpetual learning machine. Software-defined stores that continually learn from their own data will transform the shopping experience.
Intelligent supply chain: Intelligent supply chains created using digital twins, generative AI, machine learning and AI-based solvers will drive billions of dollars in labor productivity and operational efficiencies. Digital twin simulations of stores and distribution centers will optimize layouts to increase in-store sales and accelerate throughput in distribution centers.
Agentic robots working alongside associates will load and unload trucks, stock shelves and pack customer orders. Also, last-mile delivery will be enhanced with AI-based routing optimization solvers, allowing products to reach customers faster while reducing vehicle fuel costs.
]]>Generative AI applications that use text, computer code, protein chains, summaries, video and even 3D graphics require data-center-scale accelerated computing to efficiently train the large language models (LLMs) that power them.
In MLPerf Training 4.1 industry benchmarks, the NVIDIA Blackwell platform delivered impressive results on workloads across all tests — and up to 2.2x more performance per GPU on LLM benchmarks, including Llama 2 70B fine-tuning and GPT-3 175B pretraining.
In addition, NVIDIA’s submissions on the NVIDIA Hopper platform continued to hold at-scale records on all benchmarks, including a submission with 11,616 Hopper GPUs on the GPT-3 175B benchmark.
Leaps and Bounds With Blackwell
The first Blackwell training submission to the MLCommons Consortium — which creates standardized, unbiased and rigorously peer-reviewed testing for industry participants — highlights how the architecture is advancing generative AI training performance.
For instance, the architecture includes new kernels that make more efficient use of Tensor Cores. Kernels are optimized, purpose-built math operations like matrix-multiplies that are at the heart of many deep learning algorithms.
Blackwell’s higher per-GPU compute throughput and significantly larger and faster high-bandwidth memory allows it to run the GPT-3 175B benchmark on fewer GPUs while achieving excellent per-GPU performance.
Taking advantage of larger, higher-bandwidth HBM3e memory, just 64 Blackwell GPUs were able to run in the GPT-3 LLM benchmark without compromising per-GPU performance. The same benchmark run using Hopper needed 256 GPUs.
The Blackwell training results follow an earlier submission to MLPerf Inference 4.1, where Blackwell delivered up to 4x more LLM inference performance versus the Hopper generation. Taking advantage of the Blackwell architecture’s FP4 precision, along with the NVIDIA QUASAR Quantization System, the submission revealed powerful performance while meeting the benchmark’s accuracy requirements.
Relentless Optimization
NVIDIA platforms undergo continuous software development, racking up performance and feature improvements in training and inference for a wide variety of frameworks, models and applications.
In this round of MLPerf training submissions, Hopper delivered a 1.3x improvement on GPT-3 175B per-GPU training performance since the introduction of the benchmark.
NVIDIA also submitted large-scale results on the GPT-3 175B benchmark using 11,616 Hopper GPUs connected with NVIDIA NVLink and NVSwitch high-bandwidth GPU-to-GPU communication and NVIDIA Quantum-2 InfiniBand networking.
NVIDIA Hopper GPUs have more than tripled scale and performance on the GPT-3 175B benchmark since last year. In addition, on the Llama 2 70B LoRA fine-tuning benchmark, NVIDIA increased performance by 26% using the same number of Hopper GPUs, reflecting continued software enhancements.
NVIDIA’s ongoing work on optimizing its accelerated computing platforms enables continued improvements in MLPerf test results — driving performance up in containerized software, bringing more powerful computing to partners and customers on existing platforms and delivering more return on their platform investment.
Partnering Up
NVIDIA partners, including system makers and cloud service providers like ASUSTek, Azure, Cisco, Dell, Fujitsu, Giga Computing, Lambda Labs, Lenovo, Oracle Cloud, Quanta Cloud Technology and Supermicro also submitted impressive results to MLPerf in this latest round.
A founding member of MLCommons, NVIDIA sees the role of industry-standard benchmarks and benchmarking best practices in AI computing as vital. With access to peer-reviewed, streamlined comparisons of AI and HPC platforms, companies can keep pace with the latest AI computing innovations and access crucial data that can help guide important platform investment decisions.
Learn more about the latest MLPerf results on the NVIDIA Technical Blog.
]]>To provide high-quality medical care to its population — around 30% of whom are 65 or older — Japan is pursuing sovereign AI initiatives supporting nearly every aspect of healthcare.
AI tools trained on country-specific data and local compute infrastructure are supercharging the abilities of Japan’s clinicians and researchers so they can care for patients, amid an expected shortage of nearly 500,000 healthcare workers by next year.
Breakthrough technology deployments by the country’s healthcare leaders — including in AI-accelerated drug discovery, genomic medicine, healthcare imaging and robotics — are highlighted at the NVIDIA AI Summit Japan, taking place in Tokyo through Nov. 13.
Powered by NVIDIA AI computing platforms like the Tokyo-1 NVIDIA DGX supercomputer, these applications were developed using domain-specific platforms such as NVIDIA BioNeMo for drug discovery, NVIDIA MONAI for medical imaging, NVIDIA Parabricks for genomics and NVIDIA Holoscan for healthcare robotics.
Drug Discovery AI Factories Deepen Understanding, Accuracy and Speed
NVIDIA is supporting Japan’s pharmaceutical market — one of the three largest in the world — with NVIDIA BioNeMo, an end-to-end platform that enables drug discovery researchers to develop and deploy AI models for generating biological intelligence from biomolecular data.
BioNeMo includes a customizable, modular programming framework and NVIDIA NIM microservices for optimized AI inference. New models include AlphaFold2, which predicts the 3D structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence; DiffDock, which predicts the 3D structure of a molecule interacting with a protein; and RFdiffusion, which designs novel protein structures likely to bind with a target molecule.
The platform also features BioNeMo Blueprints, a catalog of customizable reference AI workflows to help developers scale biomolecular AI models to enterprise-grade applications.
The NIM microservice for AlphaFold2 now integrates MMSeqs2-GPU, an evolutionary information retrieval tool that accelerates the traditional AlphaFold2 pipeline by 5x. Led by researchers at Seoul National University, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz and NVIDIA, this integration enables protein structure prediction in 8 minutes instead of 40 minutes.
At AI Summit Japan, TetraScience, a company that engineers AI-native scientific datasets, announced a collaboration with NVIDIA to industrialize the production of scientific AI use cases to accelerate and improve workflows across the life sciences value chain.
For example, choosing an optimal cell line to produce biologic therapies such as vaccines and monoclonal antibodies is a critical but time-consuming step. TetraScience’s new Lead Clone Assistant uses BioNeMo tools, including the NVIDIA VISTA-2D foundation model for cell segmentation and the Geneformer model for gene expression analysis, to reduce lead clone selection to hours instead of weeks.
Tokyo-based Astellas Pharma uses BioNeMo biomolecular AI models such as ESM-1nv, ESM-2nv and DNABERT to accelerate biologics research. Its AI models are used to generate novel molecular structures, predict how those molecules will bind to target proteins and optimize them to more effectively bind to those target proteins.
Using the BioNeMo framework, Astellas has accelerated chemical molecule generation by more than 30x. The company plans to use BioNeMo NIM microservices to further advance its work.
Japan’s Pharma Companies and Research Institutions Advance Drug Research and Development
Astellas, Daiichi-Sankyo and Ono Pharmaceutical are leading Japanese pharma companies harnessing the Tokyo-1 system, an NVIDIA DGX AI supercomputer built in collaboration with Xeureka, a subsidiary of the Japanese business conglomerate Mitsui & Co, to build AI models for drug discovery. Xeureka is using Tokyo-1 to accelerate AI model development and molecular simulations.
Xeureka is also using NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs to explore the application of confidential computing to enhance the ability of pharmaceutical companies to collaborate on large AI model training while protecting proprietary datasets.
To further support disease and precision medicine research, genomics researchers across Japan have adopted the NVIDIA Parabricks software suite to accelerate secondary analysis of DNA and RNA data.
Among them is the University of Tokyo Human Genome Center, the main academic institution working on a government-led whole genome project focused on cancer research. The initiative will help researchers identify gene variants unique to Japan’s population and support the development of precision therapeutics.
The genome center is also exploring the use of Giraffe, a tool now available via Parabricks v4.4 that enables researchers to map genome sequences to a pangenome, a reference genome that represents diverse populations.
AI Scanners and Scopes Give Radiologists and Surgeons Real-Time Superpowers
Japan’s healthcare innovators are building AI-augmented systems to support radiologists and surgeons.
Fujifilm has developed an AI application in collaboration with NVIDIA to help surgeons perform surgery more efficiently.
This application uses an AI model developed using NVIDIA DGX systems to convert CT images into 3D simulations to support surgery.
Olympus recently collaborated with NVIDIA and telecommunications company NTT to demonstrate how cloud-connected endoscopes can efficiently run image processing and AI applications in real time. The endoscopes featured NVIDIA Jetson Orin modules for edge computing and connected to a cloud server using the NTT communication platform’s IOWN All-Photonics Network, which introduces photonics-based technology across the network to enable lower power consumption, greater capacity and lower latency.
NVIDIA is also supporting real-time AI-powered robotic systems for radiology and surgery in Japan with Holoscan, a sensor processing platform that streamlines AI model and application development for real-time insights. Holoscan includes a catalog of AI reference workflows for applications including endoscopy and ultrasound analysis.
A neurosurgeon at Showa University, a medical school with multiple campuses across Japan, has adopted Holoscan and the NVIDIA IGX platform for industrial-grade edge AI to develop a surgical microscopy application that takes video footage from surgical scopes and converts it into 3D imagery in real time using AI. With access to 3D reconstructions, surgeons can more easily locate tumors and key structures in the brain to improve the efficiency of procedures.
Japanese surgical AI companies including AI Medical Service (AIM), Anaut, iMed Technologies and Jmees are investigating the use of Holoscan to power applications that provide diagnostic support for endoscopists and surgeons. These applications could detect anatomical structures like organs in real time, with the potential to reduce injury risks, identify conditions such as gastrointestinal cancers and brain hemorrhages, and provide immediate insights to help doctors prepare for and conduct surgeries.
Scaling Healthcare With Digital Health Agents
Older adults have higher rates of chronic conditions and use healthcare services the most — so to keep up with its aging population, Japan-based companies are at the forefront of developing digital health systems to augment patient care.
Fujifilm has launched NURA, a group of health screening centers with AI-augmented medical examinations designed to help doctors test for cancer and chronic diseases with faster examinations and lower radiation doses for CT scans.
Developed using NVIDIA DGX systems, the tool incorporates large language models that create text summaries of medical images. The AI models run on NVIDIA RTX GPUs for inference. Fujifilm is also evaluating the use of MONAI, NeMo and NIM microservices.
To learn more about NVIDIA’s collaborations with Japan’s healthcare ecosystem, watch the NVIDIA AI Summit on-demand session by Kimberly Powell, the company’s vice president of healthcare.
]]>Established 77 years ago, Mitsui & Co stays vibrant by building businesses and ecosystems with new technologies like generative AI and confidential computing.
Digital transformation takes many forms at the Tokyo-based conglomerate with 16 divisions. In one case, it’s an autonomous trucking service, in another it’s a geospatial analysis platform. Mitsui even collaborates with a partner at the leading edge of quantum computing.
One new subsidiary, Xeureka, aims to accelerate R&D in healthcare, where it can take more than a billion dollars spent over a decade to bring to market a new drug.
“We create businesses using new digital technology like AI and confidential computing,” said Katsuya Ito, a project manager in Mitsui’s digital transformation group. “Most of our work is done in collaboration with tech companies — in this case NVIDIA and Fortanix,” a San Francisco based security software company.
In Pursuit of Big Data
Though only three years old, Xeureka already completed a proof of concept addressing one of drug discovery’s biggest problems — getting enough data.
Speeding drug discovery requires powerful AI models built with datasets larger than most pharmaceutical companies have on hand. Until recently, sharing across companies has been unthinkable because data often contains private patient information as well as chemical formulas proprietary to the drug company.
Enter confidential computing, a way of processing data in a protected part of a GPU or CPU that acts like a black box for an organization’s most important secrets.
To ensure their data is kept confidential at all times, banks, government agencies and even advertisers are using the technology that’s backed by a consortium of some of the world’s largest companies.
A Proof of Concept for Privacy
To validate that confidential computing would allow its customers to safely share data, Xeureka created two imaginary companies, each with a thousand drug candidates. Each company’s dataset was used separately to train an AI model to predict the chemicals’ toxicity levels. Then the data was combined to train a similar, but larger AI model.
Xeureka ran its test on NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs using security management software from Fortanix, one of the first startups to support confidential computing.
The H100 GPUs support a trusted execution environment with hardware-based engines that ensure and validate confidential workloads are protected while in use on the GPU, without compromising performance. The Fortanix software manages data sharing, encryption keys and the overall workflow.
Up to 74% Higher Accuracy
The results were impressive. The larger model’s predictions were 65-74% more accurate, thanks to use of the combined datasets.
The models created by a single company’s data showed instability and bias issues that were not present with the larger model, Ito said.
“Confidential computing from NVIDIA and Fortanix essentially alleviates the privacy and security concerns while also improving model accuracy, which will prove to be a win-win situation for the entire industry,” said Xeureka’s CTO, Hiroki Makiguchi, in a Fortanix press release.
An AI Supercomputing Ecosystem
Now, Xeureka is exploring broad applications of this technology in drug discovery research, in collaboration with the community behind Tokyo-1, its GPU-accelerated AI supercomputer. Announced in February, Tokyo-1 aims to enhance the efficiency of pharmaceutical companies in Japan and beyond.
Initial projects may include collaborations to predict protein structures, screen ligand-base pairs and accelerate molecular dynamics simulations with trusted services. Tokyo-1 users can harness large language models for chemistry, protein, DNA and RNA data formats through the NVIDIA BioNeMo drug discovery microservices and framework.
It’s part of Mitsui’s broader strategic growth plan to develop software and services for healthcare, such as powering Japan’s $100 billion pharma industry, the world’s third largest following the U.S. and China.
Xeueka’s services will include using AI to quickly screen billions of drug candidates, to predict how useful molecules will bind with proteins and to simulate detailed chemical behaviors.
To learn more, read about NVIDIA Confidential Computing and NVIDIA BioNeMo, an AI platform for drug discovery.
]]>Consulting giants including Accenture, Deloitte, EY Strategy and Consulting Co., Ltd. (or EY Japan), FPT, Kyndryl and Tata Consultancy Services Japan (TCS Japan) are working with NVIDIA to establish innovation centers in Japan to accelerate the nation’s goal of embracing enterprise AI and physical AI across its industrial landscape.
The centers will use NVIDIA AI Enterprise software, local language models and NVIDIA NIM microservices to help clients in Japan advance the development and deployment of AI agents tailored to their industries’ respective needs, boosting productivity with a digital workforce.
Using the NVIDIA Omniverse platform, Japanese firms can develop digital twins and simulate complex physical AI systems, driving innovation in manufacturing, robotics and other sectors.
Like many nations, Japan is navigating complex social and demographic challenges, which is leading to a smaller workforce as older generations retire. Leaning into its manufacturing and robotics leadership, the country is seeking opportunities to solve these challenges using AI.
The Japanese government in April published a paper on its aims to become “the world’s most AI-friendly country.” AI adoption is strong and growing, as IDC reports that the Japanese AI systems market reached approximately $5.9 billion this year, with a year-on-year growth rate of 31.2%.1
The consulting giants’ initiatives and activities include:
- Accenture has established the Accenture NVIDIA Business Group and will provide solutions and services incorporating a Japanese large language model (LLM), which uses NVIDIA NIM and NVIDIA NeMo, as a Japan-specific offering. In addition, Accenture will deploy agentic AI solutions based on Accenture AI Refinery to all industries in Japan, accelerating total enterprise reinvention for its clients. In the future, Accenture plans to build new services using NVIDIA AI Enterprise and Omniverse at Accenture Innovation Hub Tokyo.
- Deloitte is establishing its AI Experience Center in Tokyo, which will serve as an executive briefing center to showcase generative AI solutions built on NVIDIA technology. This facility builds on the Deloitte Japan NVIDIA Practice announced in June and will allow clients to experience firsthand how AI can revolutionize their operations. The center will also offer NVIDIA AI and Omniverse Blueprints to help enterprises in Japan adopt agentic AI effectively.
- EY Strategy and Consulting Co., Ltd (EY Japan) is developing a multitude of digital transformation (DX) solutions in Japan across diverse industries including finance, retail, media and manufacturing. The new EY Japan DX offerings will be built with NVIDIA AI Enterprise to serve the country’s growing demand for digital twins, 3D applications, multimodal AI and generative AI.
- FPT is launching FPT AI Factory in Japan with NVIDIA Hopper GPUs and NVIDIA AI Enterprise software to support the country’s AI transformation by using business data in a secure, sovereign environment. FPT is integrating the NVIDIA NeMo framework with FPT AI Studio for building, pretraining and fine-tuning generative AI models, including FPT’s multi-language LLM, named Saola. In addition, to provide end-to-end AI integration services, FPT plans to train over 1,000 software engineers and consultants domestically in Japan, and over 7,000 globally by 2026.
- IT infrastructure services provider Kyndryl has launched a dedicated AI private cloud in Japan. Built in collaboration with Dell Technologies using the Dell AI Factory with NVIDIA, this new AI private cloud will provide a controlled, secure and sovereign location for customers to develop, test and plan implementation of AI on the end-to-end NVIDIA AI platform, including NVIDIA accelerated computing and networking, as well as the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software.
- TCS Japan will begin offering its TCS global AI offerings built on the full NVIDIA AI stack in the automotive and manufacturing industries. These solutions will be hosted in its showcase centers at TCS Japan’s Azabudai office in Tokyo.
Located in the Tokyo and Kansai metropolitan areas, these new consulting centers offer hands-on experience with NVIDIA’s latest technologies and expert guidance — helping accelerate AI transformation, solve complex social challenges and support the nation’s economic growth.
To learn more, watch the NVIDIA AI Summit Japan fireside chat with NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang.
Editor’s note: IDC figures are sourced to IDC, 2024 Domestic AI System Market Forecast Announced, April 2024. The IDC forecast amount was converted to USD by NVIDIA, while the CAGR (31.2%) was calculated based on JPY.
]]>Lifelike digital humans engage with audiences in real time. Autonomous systems streamline complex logistics. And AI-driven language tools break down communication barriers on the fly.
This isn’t sci-fi. This is Tokyo’s startup scene.
Supercharged by AI — and world-class academic and industrial might — the region has become a global innovation hub. And the NVIDIA Inception program is right in the middle of it.
With over 370 AI-driven startups in the program and a 250,000-person strong NVIDIA developer community, Japan’s AI startup ecosystem is as bold as it is fast-moving.
This week’s NVIDIA AI Summit Japan puts these achievements in the spotlight, capturing the region’s relentless innovation momentum.
NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang and SoftBank Group Chairman and CEO Masayoshi Son opened the summit with a fireside chat to discuss AI’s transformative role, with Jensen diving into Japan’s growing AI ecosystem and its push toward sovereign AI.
Sessions followed with leaders from METI (Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry), the University of Tokyo and other key players. Their success is no accident.
Tokyo’s academic powerhouses, global technology and industrial giants, and technology-savvy population of 14 million, provide the underpinnings of a global AI hub that stretches from the bustling startup scene in Shibuya to new hotbeds of tech development in Chiyoda and beyond.
Supercharging Japan’s Creative Class
Iconic works from anime to manga have not only redefined entertainment in Japan — they’ve etched themselves into global culture, inspiring fans across continents, languages and generations.
Now, Japan’s vibrant visual pop culture is spilling into AI, finding fresh ways to surprise and connect with audiences.
Take startup AiHUB’s digital celebrity Sali.
Sali isn’t just a character in the traditional sense. She’s a digital being with presence — responsive and lifelike. She blinks, she smiles, she reacts.
Here, AI is doing something quietly revolutionary, slipping under the radar to redefine how people interact with media.
At AI Summit Japan, AiHUB revealed that it will adopt the NVIDIA Avatar Cloud Engine, or ACE, in the lip-sync module of its digital human framework, providing Sali nuanced expressions and human-like emotional depth.
ACE doesn’t just make Sali relatable — it puts her in a league of characters who transcend screens and pages.
This integration reduced development and future management costs by approximately 50% while improving the expressiveness of the avatars, according to AiHUB.
SDK Adoption: From Hesitation to High Velocity
In the global tech race, success doesn’t always hinge on the heroes you’d expect.
The unsung stars here are software development kits — those bundles of tools, libraries and documentation that cut the guesswork out of innovation. And in Japan’s fast-evolving AI ecosystem, these once-overlooked SDKs are driving an improbable revolution.
For years, Japan’s tech companies treated SDKs with caution. Now, however, with AI advancing at lightspeed and NVIDIA GPUs powering the engine, SDKs have moved from a quiet corner to center stage.
Take NVIDIA NeMo, a platform for building large language models, or LLMs. It’s swiftly becoming the background for Japan’s latest wave of real-time, AI-driven communication technologies.
One company at the forefront is Kotoba Technologies, which has cracked the code on real-time speech recognition thanks to NeMo’s powerful tools.
Under a key Japanese government grant, Kotoba’s language tools don’t just capture sound — they translate it live. It’s a blend of computational heft and human ingenuity, redefining how multilingual communication happens in non-English-speaking countries like Japan.
Kotoba’s tools are used in customer call centers and for automatic meeting minutes creation across various industries. It was also used to perform live transcription during the AI Summit Japan fireside chat between Huang and Son.
And if LLMs are the engines driving Japan’s AI, then companies like APTO supply the fuel. Using NVIDIA NeMo Curator, APTO is changing the game in data annotation, handling the intensive prep work that makes LLMs effective.
By refining data quality for big clients like RIKEN, Ricoh and ORIX, APTO has mastered the fine art of sifting valuable signals from noise. Through tools like WordCountFilter — an ingenious mechanism that prunes short or unnatural sentences — it’s supercharging performance.
APTO’s data quality control boosted model accuracy scores and slashed training time.
Across Japan, developers are looking to move on AI fast, and they’re embracing SDKs to go further, faster.
The Power of Cross-Sector Synergy
The gears of Japan’s AI ecosystem increasingly turn in sync thanks to NVIDIA-powered infrastructure that enables startups to build on each other’s breakthroughs.
As Japan’s population ages, solutions like these address security needs as well as an intensifying labor shortage. Here, ugo and Asilla have taken on the challenge, using autonomous security systems to manage facilities across the country.
Asilla’s cutting-edge anomaly detection was developed with security in mind but is now finding applications in healthcare and retail. Built on the NVIDIA DeepStream and Triton Inference Server SDKs, Asilla’s tech doesn’t just identify risks — it responds to them.
In high-stakes environments, ugo and Asilla’s systems, powered by the NVIDIA Jetson platform, are already in action, identifying potential security threats and triggering real-time responses.
NVIDIA’s infrastructure is also at the heart of Kotoba Technologies’ language tools, as well as AiHUB’s lifelike digital avatars. Running on an AI backbone, these various tools seamlessly bridge media, communication and human interaction.
The Story Behind the Story: Tokyo IPC and Osaka Innovation Hub
All of these startups are part of a larger ecosystem that’s accelerating Japan’s rise as an AI powerhouse.
Leading the charge is UTokyo IPC, the wholly owned venture capital arm of the University of Tokyo, operating through its flagship accelerator program, 1stRound.
Cohosted by 18 universities and four national research institutions, this program serves as the nexus where academia and industry converge, providing hands-on guidance, resources and strategic support.
By championing the real-world deployment of seed-stage deep-tech innovations, UTokyo IPC is igniting Japan’s academic innovation landscape and setting the standard for others to follow.
Meanwhile, Osaka’s own Innovation Hub, OIH, expands this momentum beyond Tokyo, providing startups with coworking spaces and networking events. Its Startup Acceleration Program brings early-stage projects to market faster.
Fast-moving hubs like these are core to Japan’s AI ecosystem, giving startups the mentorship, funding and resources they need to go from prototype to fully commercialized product.
And through NVIDIA’s accelerated computing technologies and the Inception program, Japan’s fast-moving startups are united with AI innovators across the globe.
Image credit: ugo.
]]>From call centers to factories to hospitals, AI is sweeping Japan.
Undergirding it all: the exceptional resources of the island nation’s world-class universities and global technology leaders such as Fujitsu, The Institute of Science Tokyo, NEC and NTT.
NVIDIA software — NVIDIA AI Enterprise for building and deploying AI agents and NVIDIA Omniverse for bringing AI into the physical world — is playing a crucial role in supporting Japan’s transformation into a global hub for AI development.
The bigger picture: Japan’s journey to AI sovereignty is well underway to support the nation in building, developing and sharing AI innovations at home and across the world.
Japanese AI Pioneers to Power Homegrown Innovation
Putting Japan in a position to become a global AI leader begins with AI-driven language models. Japanese tech leaders are developing advanced AI models that can better interpret Japanese cultural and linguistic nuances.
These models enable developers to build AI applications for industries requiring high-precision outcomes, such as healthcare, finance and manufacturing.
As Japan’s tech giants support AI adoption across the country, they’re using NVIDIA AI Enterprise software.
Fujitsu’s Takane model is specifically built for high-stakes sectors like finance and security.
The model is designed to prioritize security and accuracy with Japanese data, which is crucial for sensitive fields. It excels in both domestic and international Japanese LLM benchmarks for natural Japanese expression and accuracy.
The companies plan to use NVIDIA NeMo for additional fine-tuning, and Fujitsu has tapped NVIDIA to support making Takane available as an NVIDIA NIM to broaden accessibility for the developer community.
NEC’s cotomi model uses NeMo’s parallel processing techniques for efficient model training. It’s already integrated with NEC’s solutions in finance, manufacturing, healthcare and local governments.
NTT Group is moving forward with NTT Communications’ launch of NTT’s large language model “tsuzumi,” which is accelerated with NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM for AI agent customer experiences and use cases such as document summarization.
Meanwhile, startups such as Kotoba Technologies, a Tokyo-based software developer, will unveil its Kotoba-Whisper model, built using NVIDIA NeMo for AI model building.
The transcription application built on the Kotoba-Whisper model performed live transcription during this week’s conversation between SoftBank Chairman and CEO Masayoshi Son and NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang at NVIDIA AI Summit Japan.
Kotoba Technologies reports that using NeMo’s automatic speech recognition for data preprocessing delivers superior transcription performance.
Kotoba-Whisper is already used in healthcare to create medical records from patient conversations, in customer call centers and for automatic meeting minutes creation across various industries.
These models are used by developers and researchers, especially those focusing on Japanese language AI applications.
Academic Contributions to Japan’s Sovereign AI Vision
Japanese universities, meanwhile, are powering the ongoing transformation with a wave of AI innovations.
Nagoya University’s Ruri-Large, built using NVIDIA’s Nemotron-4 340B — which is also available as a NIM microservice — is a Japanese embedding model. It achieves high document retrieval performance with high-quality synthetic data generated by Nemotron-4 340B, and it enables the enhancement of language model capabilities through retrieval-augmented generation using external, authoritative knowledge bases.
The National Institute of Informatics will introduce LLM.jp-3-13B-Instruct, a sovereign AI model developed from scratch. Supported by several Japanese government-backed programs, this model underscores the nation’s commitment to self-sufficiency in AI. It’s expected to be available as a NIM microservice soon.
The Institute of Science Tokyo and Japan’s National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, better known as AIST, will present the Llama 3.1 Swallow model. Optimized for Japanese tasks, it’s now a NIM microservice that can integrate into generative AI workflows for uses ranging from cultural research to business applications.
The University of Tokyo’s Human Genome Center uses NVIDIA AI Enterprise and NVIDIA Parabricks software for rapid genomic analysis, advancing life sciences and precision medicine.
Japan’s Tech Providers Helping Organizations Adopt AI
In addition, technology providers are working to bring NVIDIA AI technologies of all kinds to organizations across Japan.
Accenture will deploy AI agent solutions based on the Accenture AI Refinery across all industries in Japan, customizing with NVIDIA NeMo and deploying with NVIDIA NIM for a Japanese-specific solution.
Dell Technologies is deploying the Dell AI Factory with NVIDIA globally — with a key focus on the Japanese market — and will support NVIDIA NIM microservices for Japanese enterprises across various industries.
Deloitte will integrate NIM microservices that support the leading Japanese language models including LLM.jp, Kotoba, Ruri-large, Swallow and more, into its multi-agent solution.
HPE has launched HPE Private Cloud AI platform, supporting NVIDIA AI Enterprise in a private environment. This solution can be tailored for organizations looking to tap into Japan’s sovereign AI NIM microservices, meeting the needs of companies that prioritize data sovereignty while using advanced AI capabilities.
Bringing Physical AI to Industries With NVIDIA Omniverse
The proliferation of language models across academia, startups and enterprises, however, is just the start of Japan’s AI revolution.
A leading maker of industrial robots, a top automaker and a retail giant are all embracing NVIDIA Omniverse and AI, as physics-based simulation drives the next wave of automation.
Industrial automation provider Yaskawa, which has shipped 600,000 robots, is developing adaptive robots for increased autonomy. Yaskawa is now adopting NVIDIA Isaac libraries and AI models to create adaptive robot applications for factory automation and other industries such as food, logistics, medical, agriculture and more.
It’s using NVIDIA Isaac Manipulator, a reference workflow of NVIDIA-accelerated libraries and AI models, to help its developers build AI-enabled manipulators, or robot arms.
It’s also using NVIDIA FoundationPose for precise 6D pose estimation and tracking.
More broadly, NVIDIA and Yaskawa teams use AI-powered simulations and digital twin technology — powered by Omniverse — to accelerate the development and deployment of Yaskawa’s robotic solutions, saving time and resources.
Meanwhile, Toyota is looking into how to build robotic factory lines in Omniverse to improve tasks in robot motion in metal-forging processes.
And another iconic Japanese company, Seven & i Holdings, is using Omniverse to gather insights from video cameras in research to optimize retail and enhance safety.
To learn more, check out our blog on these use cases.
See notice regarding software product information.
]]>Robotics developers can greatly accelerate their work on AI-enabled robots, including humanoids, using new AI and simulation tools and workflows that NVIDIA revealed this week at the Conference for Robot Learning (CoRL) in Munich, Germany.
The lineup includes the general availability of the NVIDIA Isaac Lab robot learning framework; six new humanoid robot learning workflows for Project GR00T, an initiative to accelerate humanoid robot development; and new world-model development tools for video data curation and processing, including the NVIDIA Cosmos tokenizer and NVIDIA NeMo Curator for video processing.
The open-source Cosmos tokenizer provides robotics developers superior visual tokenization by breaking down images and videos into high-quality tokens with exceptionally high compression rates. It runs up to 12x faster than current tokenizers, while NeMo Curator provides video processing curation up to 7x faster than unoptimized pipelines.
Also timed with CoRL, NVIDIA presented 23 papers and nine workshops related to robot learning and released training and workflow guides for developers. Further, Hugging Face and NVIDIA announced they’re collaborating to accelerate open-source robotics research with LeRobot, NVIDIA Isaac Lab and NVIDIA Jetson for the developer community.
Accelerating Robot Development With Isaac Lab
NVIDIA Isaac Lab is an open-source, robot learning framework built on NVIDIA Omniverse, a platform for developing OpenUSD applications for industrial digitalization and physical AI simulation.
Developers can use Isaac Lab to train robot policies at scale. This open-source unified robot learning framework applies to any embodiment — from humanoids to quadrupeds to collaborative robots — to handle increasingly complex movements and interactions.
Leading commercial robot makers, robotics application developers and robotics research entities around the world are adopting Isaac Lab, including 1X, Agility Robotics, The AI Institute, Berkeley Humanoid, Boston Dynamics, Field AI, Fourier, Galbot, Mentee Robotics, Skild AI, Swiss-Mile, Unitree Robotics and XPENG Robotics.
Project GR00T: Foundations for General-Purpose Humanoid Robots
Building advanced humanoids is extremely difficult, demanding multilayer technological and interdisciplinary approaches to make the robots perceive, move and learn skills effectively for human-robot and robot-environment interactions.
Project GR00T is an initiative to develop accelerated libraries, foundation models and data pipelines to accelerate the global humanoid robot developer ecosystem.
Six new Project GR00T workflows provide humanoid developers with blueprints to realize the most challenging humanoid robot capabilities. They include:
- GR00T-Gen for building generative AI-powered, OpenUSD-based 3D environments
- GR00T-Mimic for robot motion and trajectory generation
- GR00T-Dexterity for robot dexterous manipulation
- GR00T-Control for whole-body control
- GR00T-Mobility for robot locomotion and navigation
- GR00T-Perception for multimodal sensing
“Humanoid robots are the next wave of embodied AI,” said Jim Fan, senior research manager of embodied AI at NVIDIA. “NVIDIA research and engineering teams are collaborating across the company and our developer ecosystem to build Project GR00T to help advance the progress and development of global humanoid robot developers.”
New Development Tools for World Model Builders
Today, robot developers are building world models — AI representations of the world that can predict how objects and environments respond to a robot’s actions. Building these world models is incredibly compute- and data-intensive, with models requiring thousands of hours of real-world, curated image or video data.
NVIDIA Cosmos tokenizers provide efficient, high-quality encoding and decoding to simplify the development of these world models. They set a new standard of minimal distortion and temporal instability, enabling high-quality video and image reconstructions.
Providing high-quality compression and up to 12x faster visual reconstruction, the Cosmos tokenizer paves the path for scalable, robust and efficient development of generative applications across a broad spectrum of visual domains.
1X, a humanoid robot company, has updated the 1X World Model Challenge dataset to use the Cosmos tokenizer.
“NVIDIA Cosmos tokenizer achieves really high temporal and spatial compression of our data while still retaining visual fidelity,” said Eric Jang, vice president of AI at 1X Technologies. “This allows us to train world models with long horizon video generation in an even more compute-efficient manner.”
Other humanoid and general-purpose robot developers, including XPENG Robotics and Hillbot, are developing with the NVIDIA Cosmos tokenizer to manage high-resolution images and videos.
NeMo Curator now includes a video processing pipeline. This enables robot developers to improve their world-model accuracy by processing large-scale text, image and video data.
Curating video data poses challenges due to its massive size, requiring scalable pipelines and efficient orchestration for load balancing across GPUs. Additionally, models for filtering, captioning and embedding need optimization to maximize throughput.
NeMo Curator overcomes these challenges by streamlining data curation with automatic pipeline orchestration, reducing processing time significantly. It supports linear scaling across multi-node, multi-GPU systems, efficiently handling over 100 petabytes of data. This simplifies AI development, reduces costs and accelerates time to market.
Advancing the Robot Learning Community at CoRL
The nearly two dozen research papers the NVIDIA robotics team released with CoRL cover breakthroughs in integrating vision language models for improved environmental understanding and task execution, temporal robot navigation, developing long-horizon planning strategies for complex multistep tasks and using human demonstrations for skill acquisition.
Groundbreaking papers for humanoid robot control and synthetic data generation include SkillGen, a system based on synthetic data generation for training robots with minimal human demonstrations, and HOVER, a robot foundation model for controlling humanoid robot locomotion and manipulation.
NVIDIA researchers will also be participating in nine workshops at the conference. Learn more about the full schedule of events.
Availability
NVIDIA Isaac Lab 1.2 is available now and is open source on GitHub. NVIDIA Cosmos tokenizer is available now on GitHub and Hugging Face. NeMo Curator for video processing will be available at the end of the month.
The new NVIDIA Project GR00T workflows are coming soon to help robot companies build humanoid robot capabilities with greater ease. Read more about the workflows on the NVIDIA Technical Blog.
Researchers and developers learning to use Isaac Lab can now access developer guides and tutorials, including an Isaac Gym to Isaac Lab migration guide.
Discover the latest in robot learning and simulation in an upcoming OpenUSD insider livestream on robot simulation and learning on Nov. 13, and attend the NVIDIA Isaac Lab office hours for hands-on support and insights.
Developers can apply to join the NVIDIA Humanoid Robot Developer Program.
]]>At the Conference for Robot Learning (CoRL) in Munich, Germany, Hugging Face and NVIDIA announced a collaboration to accelerate robotics research and development by bringing together their open-source robotics communities.
Hugging Face’s LeRobot open AI platform combined with NVIDIA AI, Omniverse and Isaac robotics technology will enable researchers and developers to drive advances across a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, healthcare and logistics.
Open-Source Robotics for the Era of Physical AI
The era of physical AI — robots understanding physical properties of environments — is here, and it’s rapidly transforming the world’s industries.
To drive and sustain this rapid innovation, robotics researchers and developers need access to open-source, extensible frameworks that span the development process of robot training, simulation and inference. With models, datasets and workflows released under shared frameworks, the latest advances are readily available for use without the need to recreate code.
Hugging Face’s leading open AI platform serves more than 5 million machine learning researchers and developers, offering tools and resources to streamline AI development. Hugging Face users can access and fine-tune the latest pretrained models and build AI pipelines on common APIs with over 1.5 million models, datasets and applications freely accessible on the Hugging Face Hub.
LeRobot, developed by Hugging Face, extends the successful paradigms from its Transformers and Diffusers libraries into the robotics domain. LeRobot offers a comprehensive suite of tools for sharing data collection, model training and simulation environments along with designs for low-cost manipulator kits.
NVIDIA’s AI technology, simulation and open-source robot learning modular framework such as NVIDIA Isaac Lab can accelerate the LeRobot’s data collection, training and verification workflow. Researchers and developers can share their models and datasets built with LeRobot and Isaac Lab, creating a data flywheel for the robotics community.
Scaling Robot Development With Simulation
Developing physical AI is challenging. Unlike language models that use extensive internet text data, physics-based robotics relies on physical interaction data along with vision sensors, which is harder to gather at scale. Collecting real-world robot data for dexterous manipulation across a large number of tasks and environments is time-consuming and labor-intensive.
Making this easier, Isaac Lab, built on NVIDIA Isaac Sim, enables robot training by demonstration or trial-and-error in simulation using high-fidelity rendering and physics simulation to create realistic synthetic environments and data. By combining GPU-accelerated physics simulations and parallel environment execution, Isaac Lab provides the ability to generate vast amounts of training data — equivalent to thousands of real-world experiences — from a single demonstration.
Generated motion data is then used to train a policy with imitation learning. After successful training and validation in simulation, the policies are deployed on a real robot, where they are further tested and tuned to achieve optimal performance.
This iterative process leverages real-world data’s accuracy and the scalability of simulated synthetic data, ensuring robust and reliable robotic systems.
By sharing these datasets, policies and models on Hugging Face, a robot data flywheel is created that enables developers and researchers to build upon each other’s work, accelerating progress in the field.
“The robotics community thrives when we build together,” said Animesh Garg, assistant professor at Georgia Tech. “By embracing open-source frameworks such as Hugging Face’s LeRobot and NVIDIA Isaac Lab, we accelerate the pace of research and innovation in AI-powered robotics.”
Fostering Collaboration and Community Engagement
The planned collaborative workflow involves collecting data through teleoperation and simulation in Isaac Lab, storing it in the standard LeRobotDataset format. Data generated using GR00T-Mimic, will then be used to train a robot policy with imitation learning, which is subsequently evaluated in simulation. Finally, the validated policy is deployed on real-world robots with NVIDIA Jetson for real-time inference.
The initial steps in this collaboration have already been taken, having shown a physical picking setup with LeRobot software running on NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano, providing a powerful, compact compute platform for deployment.
“Combining Hugging Face open-source community with NVIDIA’s hardware and Isaac Lab simulation has the potential to accelerate innovation in AI for robotics,” said Remi Cadene, principal research scientist at LeRobot.
This work builds on NVIDIA’s community contributions in generative AI at the edge, supporting the latest open models and libraries, such as Hugging Face Transformers, optimizing inference for large language models (LLMs), small language models (SLMs) and multimodal vision-language models (VLMs), along with VLM’s action-based variants of vision language action models (VLAs), diffusion policies and speech models — all with strong, community-driven support.
Together, Hugging Face and NVIDIA aim to accelerate the work of the global ecosystem of robotics researchers and developers transforming industries ranging from transportation to manufacturing and logistics.
Learn about NVIDIA’s robotics research papers at CoRL, including VLM integration for better environmental understanding, temporal navigation and long-horizon planning. Check out workshops at CoRL with NVIDIA researchers.
]]>Editor’s note: This post is part of the AI Decoded series, which demystifies AI by making the technology more accessible, and showcases new hardware, software, tools and accelerations for GeForce RTX PC and NVIDIA RTX workstation users.
As generative AI evolves and accelerates industry, a community of AI enthusiasts is experimenting with ways to integrate the powerful technology into common productivity workflows.
Applications that support community plug-ins give users the power to explore how large language models (LLMs) can enhance a variety of workflows. By using local inference servers powered by the NVIDIA RTX-accelerated llama.cpp software library, users on RTX AI PCs can integrate local LLMs with ease.
Previously, we looked at how users can take advantage of Leo AI in the Brave web browser to optimize the web browsing experience. Today, we look at Obsidian, a popular writing and note-taking application, based on the Markdown markup language, that’s useful for keeping complex and linked records for multiple projects. The app supports community-developed plug-ins that bring additional functionality, including several that enable users to connect Obsidian to a local inferencing server like Ollama or LM Studio.
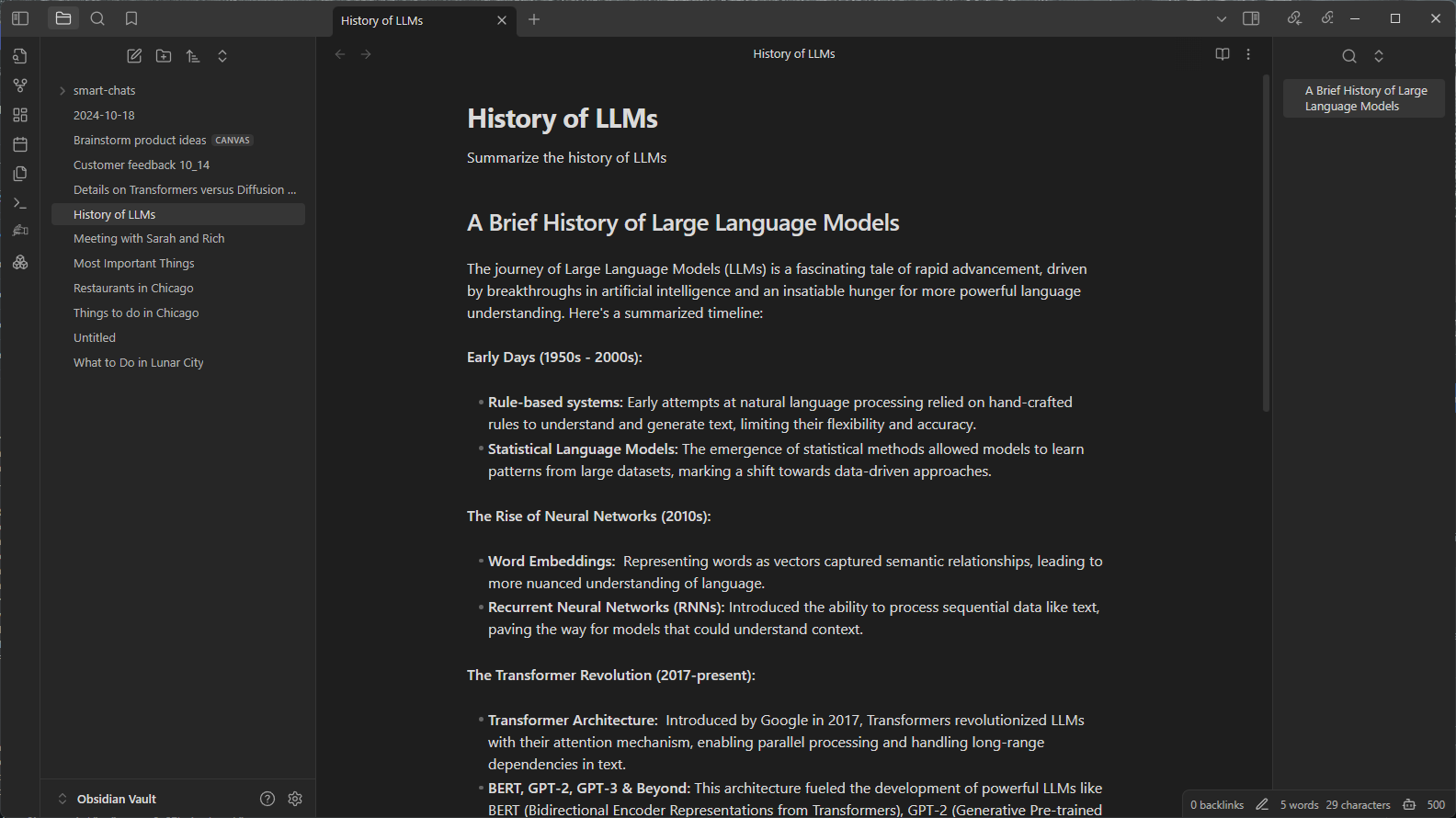
Connecting Obsidian to LM Studio only requires enabling the local server functionality in LM Studio by clicking on the “Developer” icon on the left panel, loading any downloaded model, enabling the CORS toggle and clicking “Start.” Take note of the chat completion URL from the “Developer” log console (“http://localhost:1234/v1/chat/completions” by default), as the plug-ins will need this information to connect.
Next, launch Obsidian and open the “Settings” panel. Click “Community plug-ins” and then “Browse.” There are several community plug-ins related to LLMs, but two popular options are Text Generator and Smart Connections.
- Text Generator is helpful for generating content in an Obsidian vault, like notes and summaries on a research topic.
- Smart Connections is useful for asking questions about the contents of an Obsidian vault, such as the answer to an obscure trivia question previously saved years ago.
Each plug-in has its own way of entering the LM Server URL.
For Text Generator, open the settings and select “Custom” for “Provider profile” and paste the whole URL into the “Endpoint” field. For Smart Connections, configure the settings after starting the plug-in. In the settings panel on the right side of the interface, select “Custom Local (OpenAI Format)” for the model platform. Then, enter the URL and the model name (e.g., “gemma-2-27b-instruct”) into their respective fields as they appear in LM Studio.
Once the fields are filled in, the plug-ins will function. The LM Studio user interface will also show logged activity if users are curious about what’s happening on the local server side.
Transforming Workflows With Obsidian AI Plug-Ins
Both the Text Generator and Smart Connections plug-ins use generative AI in compelling ways.
For example, imagine a user wants to plan a vacation to the fictitious destination of Lunar City and brainstorm ideas for what to do there. The user would start a new note, titled “What to Do in Lunar City.” Since Lunar City is not a real place, the query sent to the LLM will need to include a few extra instructions to guide the responses. Click the Text Generator plug-in icon, and the model will generate a list of activities to do during the trip.
Obsidian, via the Text Generator plug-in, will request LM Studio to generate a response, and in turn LM Studio will run the Gemma 2 27B model. With RTX GPU acceleration in the user’s computer, the model can quickly generate a list of things to do.
Or, suppose many years later the user’s friend is going to Lunar City and wants to know where to eat. The user may not remember the names of the places where they ate, but they can check the notes in their vault (Obsidian’s term for a collection of notes) in case they’d written something down.
Rather than looking through all of the notes manually, a user can use the Smart Connections plug-in to ask questions about their vault of notes and other content. The plug-in uses the same LM Studio server to respond to the request, and provides relevant information it finds from the user’s notes to assist the process. The plug-in does this using a technique called retrieval-augmented generation.
These are fun examples, but after spending some time with these capabilities, users can see the real benefits and improvements for everyday productivity. Obsidian plug-ins are just two ways in which community developers and AI enthusiasts are embracing AI to supercharge their PC experiences.
NVIDIA GeForce RTX technology for Windows PCs can run thousands of open-source models for developers to integrate into their Windows apps.
Learn more about the power of LLMs, Text Generation and Smart Connections by integrating Obsidian into your workflow and play with the accelerated experience available on RTX AI PCs.
Generative AI is transforming gaming, videoconferencing and interactive experiences of all kinds. Make sense of what’s new and what’s next by subscribing to the AI Decoded newsletter.
]]>Editor’s note: The name of NIM Agent Blueprints was changed to NVIDIA Blueprints in October 2024. All references to the name have been updated in this blog.
Enterprises and public sector organizations around the world are developing AI agents to boost the capabilities of workforces that rely on visual information from a growing number of devices — including cameras, IoT sensors and vehicles.
To support their work, a new NVIDIA Blueprint for video search and summarization will enable developers in virtually any industry to build visual AI agents that analyze video and image content. These agents can answer user questions, generate summaries and enable alerts for specific scenarios.
Part of NVIDIA Metropolis, a set of developer tools for building vision AI applications, the blueprint is a customizable workflow that combines NVIDIA computer vision and generative AI technologies.
Global systems integrators and technology solutions providers including Accenture, Dell Technologies and Lenovo are bringing the NVIDIA Blueprint for visual search and summarization to businesses and cities worldwide, jump-starting the next wave of AI applications that can be deployed to boost productivity and safety in factories, warehouses, shops, airports, traffic intersections and more.
Announced ahead of the Smart City Expo World Congress, the NVIDIA Blueprint gives visual computing developers a full suite of optimized software for building and deploying generative AI-powered agents that can ingest and understand massive volumes of live video streams or data archives.
Users can customize these visual AI agents with natural language prompts instead of rigid software code, lowering the barrier to deploying virtual assistants across industries and smart city applications.
NVIDIA Blueprint Harnesses Vision Language Models
Visual AI agents are powered by vision language models (VLMs), a class of generative AI models that combine computer vision and language understanding to interpret the physical world and perform reasoning tasks.
The NVIDIA Blueprint for video search and summarization can be configured with NVIDIA NIM microservices for VLMs like NVIDIA VILA, LLMs like Meta’s Llama 3.1 405B and AI models for GPU-accelerated question answering and context-aware retrieval-augmented generation. Developers can easily swap in other VLMs, LLMs and graph databases and fine-tune them using the NVIDIA NeMo platform for their unique environments and use cases.
Adopting the NVIDIA Blueprint could save developers months of effort on investigating and optimizing generative AI models for smart city applications. Deployed on NVIDIA GPUs at the edge, on premises or in the cloud, it can vastly accelerate the process of combing through video archives to identify key moments.
In a warehouse environment, an AI agent built with this workflow could alert workers if safety protocols are breached. At busy intersections, an AI agent could identify traffic collisions and generate reports to aid emergency response efforts. And in the field of public infrastructure, maintenance workers could ask AI agents to review aerial footage and identify degrading roads, train tracks or bridges to support proactive maintenance.
Beyond smart spaces, visual AI agents could also be used to summarize videos for people with impaired vision, automatically generate recaps of sporting events and help label massive visual datasets to train other AI models.
The video search and summarization workflow joins a collection of NVIDIA Blueprints that make it easy to create AI-powered digital avatars, build virtual assistants for personalized customer service and extract enterprise insights from PDF data.
NVIDIA Blueprints are free for developers to experience and download, and can be deployed in production across accelerated data centers and clouds with NVIDIA AI Enterprise, an end-to-end software platform that accelerates data science pipelines and streamlines generative AI development and deployment.
AI Agents to Deliver Insights From Warehouses to World Capitals
Enterprise and public sector customers can also harness the full collection of NVIDIA Blueprints with the help of NVIDIA’s partner ecosystem.
Global professional services company Accenture has integrated NVIDIA Blueprints into its Accenture AI Refinery, which is built on NVIDIA AI Foundry and enables customers to develop custom AI models trained on enterprise data.
Global systems integrators in Southeast Asia — including ITMAX in Malaysia and FPT in Vietnam — are building AI agents based on the video search and summarization NVIDIA Blueprint for smart city and intelligent transportation applications.
Developers can also build and deploy NVIDIA Blueprints on NVIDIA AI platforms with compute, networking and software provided by global server manufacturers.
Dell will use VLM and agent approaches with Dell’s NativeEdge platform to enhance existing edge AI applications and create new edge AI-enabled capabilities. Dell Reference Designs for the Dell AI Factory with NVIDIA and the NVIDIA Blueprint for video search and summarization will support VLM capabilities in dedicated AI workflows for data center, edge and on-premises multimodal enterprise use cases.
NVIDIA Blueprints are also incorporated in Lenovo Hybrid AI solutions powered by NVIDIA.
Companies like K2K, a smart city application provider in the NVIDIA Metropolis ecosystem, will use the new NVIDIA Blueprint to build AI agents that analyze live traffic cameras in real time. This will enable city officials to ask questions about street activity and receive recommendations on ways to improve operations. The company also is working with city traffic managers in Palermo, Italy, to deploy visual AI agents using NIM microservices and NVIDIA Blueprints.
Discover more about the NVIDIA Blueprint for video search and summarization by visiting the NVIDIA booth at the Smart Cities Expo World Congress, taking place in Barcelona through Nov. 7.
Learn how to build a visual AI agent and get started with the blueprint.
]]>