Editor’s note: This post is part of the AI Decoded series, which demystifies AI by making the technology more accessible, and showcases new hardware, software, tools and accelerations for GeForce RTX PC and NVIDIA RTX workstation users.
Generative AI has transformed the way people bring ideas to life. Agentic AI takes this one step further — using sophisticated, autonomous reasoning and iterative planning to help solve complex, multi-step problems.
AnythingLLM is a customizable open-source desktop application that lets users seamlessly integrate large language model (LLM) capabilities into various applications locally on their PCs. It enables users to harness AI for tasks such as content generation, summarization and more, tailoring tools to meet specific needs.
Accelerated on NVIDIA RTX AI PCs, AnythingLLM has launched a new Community Hub where users can share prompts, slash commands and AI agent skills while experimenting with building and running AI agents locally.
Autonomously Solve Complex, Multi-Step Problems With Agentic AI
AI agents can take chatbot capabilities further. They typically understand the context of the tasks and can analyze challenges and develop strategies — and some can even fully execute assigned tasks.
For example, while a chatbot could answer a prompt asking for a restaurant recommendation, an AI agent could even surface the restaurant’s phone number for a reservation and add reminders to the user’s calendar.
Agents help achieve big-picture goals and don’t get bogged down at the task level. There are many agentic apps in development to tackle to-do lists, manage schedules, help organize tasks, automate email replies, recommend personalized workout plans or plan trips.
Once prompted, an AI agent can gather and process data from various sources, including databases. It can use an LLM for reasoning — for example, to understand the task — then generate solutions and specific functions. If integrated with external tools and software, an AI agent can next execute the task.
Some sophisticated agents can even be improved through a feedback loop. When the data it generates is fed back into the system, the AI agent becomes smarter and faster.
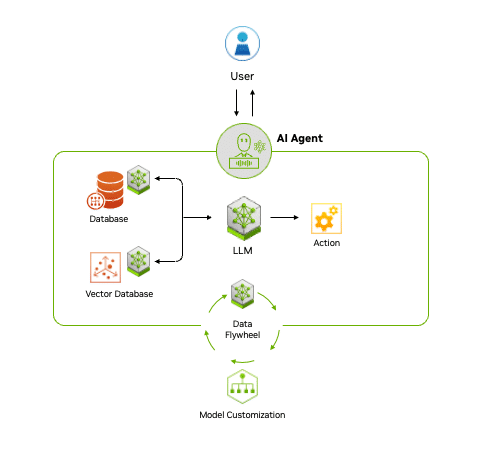
Accelerated by NVIDIA RTX AI PCs, these agents can perform inferencing and execute tasks faster than any other PC. Users can operate the agent locally to help ensure data privacy, even without an internet connection.
AnythingLLM: A Community Effort, Accelerated by RTX
The AI community is already diving into the possibilities of agentic AI, experimenting with ways to create smarter, more capable systems.
Applications like AnythingLLM let developers easily build, customize and unlock agentic AI with their favorite models — like Llama and Mistral — as well as with other tools, such as Ollama and LMStudio. AnythingLLM is accelerated on RTX-powered AI PCs and workstations with high-performance Tensor Cores, dedicated hardware that provides the compute performance needed to run the latest and most demanding AI models.
AnythingLLM is designed to make working with AI seamless, productive and accessible to everyone. It allows users to chat with their documents using intuitive interfaces, use AI agents to handle complex and custom tasks, and run cutting-edge LLMs locally on RTX-powered PCs and workstations. This means unlocked access to local resources, tools and applications that typically can’t be integrated with cloud- or browser-based applications, or those that require extensive setup and knowledge to build. By tapping into the power of NVIDIA RTX GPUs, AnythingLLM delivers faster, smarter and more responsive AI for a variety of workflows — all within a single desktop application.
AnythingLLM’s Community Hub lets AI enthusiasts easily access system prompts that can help steer LLM behavior, discover productivity-boosting slash commands, build specialized AI agent skills for unique workflows and custom tools, and access on-device resources.
Some example agent skills that are available in the Community Hub include Microsoft Outlook email assistants, calendar agents, web searches and home assistant controllers, as well as agents for populating and even integrating custom application programming interface endpoints and services for a specific use case.
By enabling AI enthusiasts to download, customize and use agentic AI workflows on their own systems with full privacy, AnythingLLM is fueling innovation and making it easier to experiment with the latest technologies — whether building a spreadsheet assistant or tackling more advanced workflows.
Experience AnythingLLM now.
Powered by People, Driven by Innovation
AnythingLLM showcases how AI can go beyond answering questions to actively enhancing productivity and creativity. Such applications illustrate AI’s move toward becoming an essential collaborator across workflows.
Agentic AI’s potential applications are vast and require creativity, expertise and computing capabilities. NVIDIA RTX AI PCs deliver peak performance for running agents locally, whether accomplishing simple tasks like generating and distributing content, or managing more complex use cases such as orchestrating enterprise software.
Learn more and get started with agentic AI.
Generative AI is transforming gaming, videoconferencing and interactive experiences of all kinds. Make sense of what’s new and what’s next by subscribing to the AI Decoded newsletter.
]]>Editor’s note: This post is the first in the AI On blog series, which explores the latest techniques and real-world applications of agentic AI, chatbots and copilots. The series will also highlight the NVIDIA software and hardware powering advanced AI agents, which form the foundation of AI query engines that gather insights and perform tasks to transform everyday experiences and reshape industries.
Whether it’s getting a complex service claim resolved or having a simple purchase inquiry answered, customers expect timely, accurate responses to their requests.
AI agents can help organizations meet this need. And they can grow in scope and scale as businesses grow, helping keep customers from taking their business elsewhere.
AI agents can be used as virtual assistants, which use artificial intelligence and natural language processing to handle high volumes of customer service requests. By automating routine tasks, AI agents ease the workload on human agents, allowing them to focus on tasks requiring a more personal touch.
AI-powered customer service tools like chatbots have become table stakes across every industry looking to increase efficiency and keep buyers happy. According to a recent IDC study on conversational AI, 41% of organizations use AI-powered copilots for customer service and 60% have implemented them for IT help desks.
Now, many of those same industries are looking to adopt agentic AI, semi-autonomous tools that have the ability to perceive, reason and act on more complex problems.
How AI Agents Enhance Customer Service
A primary value of AI-powered systems is the time they free up by automating routine tasks. AI agents can perform specific tasks, or agentic operations, essentially becoming part of an organization’s workforce — working alongside humans who can focus on more complex customer issues.
AI agents can handle predictive tasks and problem-solve, can be trained to understand industry-specific terms and can pull relevant information from an organization’s knowledge bases, wherever that data resides.
With AI agents, companies can:
- Boost efficiency: AI agents handle common questions and repetitive tasks, allowing support teams to prioritize more complicated cases. This is especially useful during high-demand periods.
- Increase customer satisfaction: Faster, more personalized interactions result in happier and more loyal customers. Consistent and accurate support improves customer sentiment and experience.
- Scale Easily: Equipped to handle high volumes of customer support requests, AI agents scale effortlessly with growing businesses, reducing customer wait times and resolving issues faster.
AI Agents for Customer Service Across Industries
AI agents are transforming customer service across sectors, helping companies enhance customer conversations, achieve high-resolution rates and improve human representative productivity.
For instance, ServiceNow recently introduced IT and customer service management AI agents to boost productivity by autonomously solving many employee and customer issues. Its agents can understand context, create step-by-step resolutions and get live agent approvals when needed.
To improve patient care and reduce preprocedure anxiety, The Ottawa Hospital is using AI agents that have consistent, accurate and continuous access to information. The agent has the potential to improve patient care and reduce administrative tasks for doctors and nurses.
The city of Amarillo, Texas, uses a multilingual digital assistant named Emma to provide its residents with 24/7 support. Emma brings more effective and efficient disbursement of important information to all residents, including the one-quarter who don’t speak English.
AI agents meet current customer service demands while preparing organizations for the future.
Key Steps for Designing AI Virtual Assistants for Customer Support
AI agents for customer service come in a wide range of designs, from simple text-based virtual assistants that resolve customer issues, to animated avatars that can provide a more human-like experience.
Digital human interfaces can add warmth and personality to the customer experience. These agents respond with spoken language and even animated avatars, enhancing service interactions with a touch of real-world flair. A digital human interface lets companies customize the assistant’s appearance and tone, aligning it with the brand’s identity.
There are three key building blocks to creating an effective AI agent for customer service:
- Collect and organize customer data: AI agents need a solid base of customer data (such as profiles, past interactions, and transaction histories) to provide accurate, context-aware responses.
- Use memory functions for personalization: Advanced AI systems remember past interactions, allowing agents to deliver personalized support that feels human.
- Build an operations pipeline: Customer service teams should regularly review feedback and update the AI agent’s responses to ensure it’s always improving and aligned with business goals.
Powering AI Agents With NVIDIA NIM Microservices
NVIDIA NIM microservices power AI agents by enabling natural language processing, contextual retrieval and multilingual communication. This allows AI agents to deliver fast, personalized and accurate support tailored to diverse customer needs.
Key NVIDIA NIM microservices for customer service agents include:
NVIDIA NIM for Large Language Models — Microservices that bring advanced language models to applications and enable complex reasoning, so AI agents can understand complicated customer queries.
NVIDIA NeMo Retriever NIM — Embedding and reranking microservices that support retrieval-augmented generation pipelines allow virtual assistants to quickly access enterprise knowledge bases and boost retrieval performance by ranking relevant knowledge-base articles and improving context accuracy.
NVIDIA NIM for Digital Humans — Microservices that enable intelligent, interactive avatars to understand speech and respond in a natural way. NVIDIA Riva NIM microservices for text-to-speech, automatic speech recognition (ASR), and translation services enable AI agents to communicate naturally across languages. The recently released Riva NIM microservices for ASR enable additional multilingual enhancements. To build realistic avatars, Audio2Face NIM converts streamed audio to facial movements for real-time lip syncing. 2D and 3D Audio2Face NIM microservices support varying use cases.
Getting Started With AI Agents for Customer Service
NVIDIA AI Blueprints make it easy to start building and setting up virtual assistants by offering ready-made workflows and tools to accelerate deployment. Whether for a simple AI-powered chatbot or a fully animated digital human interface, the blueprints offer resources to create AI assistants that are scalable, aligned with an organization’s brand and deliver a responsive, efficient customer support experience.
Editor’s note: IDC figures are sourced to IDC, Market Analysis Perspective: Worldwide Conversational AI Tools and Technologies, 2024 US51619524, Sept 2024
]]>Since the advent of the computer age, industries have been so awash in stored data that most of it never gets put to use.
This data is estimated to be in the neighborhood of 120 zettabytes — the equivalent of trillions of terabytes, or more than 120x the amount of every grain of sand on every beach around the globe. Now, the world’s industries are putting that untamed data to work by building and customizing large language models (LLMs).
As 2025 approaches, industries such as healthcare, telecommunications, entertainment, energy, robotics, automotive and retail are using those models, combining it with their proprietary data and gearing up to create AI that can reason.
The NVIDIA experts below focus on some of the industries that deliver $88 trillion worth of goods and services globally each year. They predict that AI that can harness data at the edge and deliver near-instantaneous insights is coming to hospitals, factories, customer service centers, cars and mobile devices near you.
But first, let’s hear AI’s predictions for AI. When asked, “What will be the top trends in AI in 2025 for industries?” both Perplexity and ChatGPT 4.0 responded that agentic AI sits atop the list alongside edge AI, AI cybersecurity and AI-driven robots.
Agentic AI is a new category of generative AI that operates virtually autonomously. It can make complex decisions and take actions based on continuous learning and analysis of vast datasets. Agentic AI is adaptable, has defined goals and can correct itself, and can chat with other AI agents or reach out to a human for help.
Now, hear from NVIDIA experts on what to expect in the year ahead:

Kimberly Powell
Vice President of Healthcare
Human-robotic interaction: Robots will assist human clinicians in a variety of ways, from understanding and responding to human commands, to performing and assisting in complex surgeries.
It’s being made possible by digital twins, simulation and AI that train and test robotic systems in virtual environments to reduce risks associated with real-world trials. It also can train robots to react in virtually any scenario, enhancing their adaptability and performance across different clinical situations.
New virtual worlds for training robots to perform complex tasks will make autonomous surgical robots a reality. These surgical robots will perform complex surgical tasks with precision, reducing patient recovery times and decreasing the cognitive workload for surgeons.
Digital health agents: The dawn of agentic AI and multi-agent systems will address the existential challenges of workforce shortages and the rising cost of care.
Administrative health services will become digital humans taking notes for you or making your next appointment — introducing an era of services delivered by software and birthing a service-as-a-software industry.
Patient experience will be transformed with always-on, personalized care services while healthcare staff will collaborate with agents that help them reduce clerical work, retrieve and summarize patient histories, and recommend clinical trials and state-of-the-art treatments for their patients.
Drug discovery and design AI factories: Just as ChatGPT can generate an email or a poem without putting a pen to paper for trial and error, generative AI models in drug discovery can liberate scientific thinking and exploration.
Techbio and biopharma companies have begun combining models that generate, predict and optimize molecules to explore the near-infinite possible target drug combinations before going into time-consuming and expensive wet lab experiments.
The drug discovery and design AI factories will consume all wet lab data, refine AI models and redeploy those models — improving each experiment by learning from the previous one. These AI factories will shift the industry from a discovery process to a design and engineering one.
 Rev Lebaredian
Rev Lebaredian
Vice President of Omniverse and Simulation Technology
Let’s get physical (AI, that is): Getting ready for AI models that can perceive, understand and interact with the physical world is one challenge enterprises will race to tackle.
While LLMs require reinforcement learning largely in the form of human feedback, physical AI needs to learn in a “world model” that mimics the laws of physics. Large-scale physically based simulations are allowing the world to realize the value of physical AI through robots by accelerating the training of physical AI models and enabling continuous training in robotic systems across every industry.
Cheaper by the dozen: In addition to their smarts (or lack thereof), one big factor that has slowed adoption of humanoid robots has been affordability. As agentic AI brings new intelligence to robots, though, volume will pick up and costs will come down sharply. The average cost of industrial robots is expected to drop to $10,800 in 2025, down sharply from $46K in 2010 to $27K in 2017. As these devices become significantly cheaper, they’ll become as commonplace across industries as mobile devices are.
 Deepu Talla
Deepu Talla
Vice President of Robotics and Edge Computing
Redefining robots: When people think of robots today, they’re usually images or content showing autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), manipulator arms or humanoids. But tomorrow’s robots are set to be an autonomous system that perceives, reasons, plans and acts — then learns.
Soon we’ll be thinking of robots embodied everywhere from surgical rooms and data centers to warehouses and factories. Even traffic control systems or entire cities will be transformed from static, manually operated systems to autonomous, interactive systems embodied by physical AI.
The rise of small language models: To improve the functionality of robots operating at the edge, expect to see the rise of small language models that are energy-efficient and avoid latency issues associated with sending data to data centers. The shift to small language models in edge computing will improve inference in a range of industries, including automotive, retail and advanced robotics.
 Kevin Levitt
Kevin Levitt
Global Director of Financial Services
AI agents boost firm operations: AI-powered agents will be deeply integrated into the financial services ecosystem, improving customer experiences, driving productivity and reducing operational costs.
AI agents will take every form based on each financial services firm’s needs. Human-like 3D avatars will take requests and interact directly with clients, while text-based chatbots will summarize thousands of pages of data and documents in seconds to deliver accurate, tailored insights to employees across all business functions.
AI factories become table stakes: AI use cases in the industry are exploding. This includes improving identity verification for anti-money laundering and know-your-customer regulations, reducing false positives for transaction fraud and generating new trading strategies to improve market returns. AI also is automating document management, reducing funding cycles to help consumers and businesses on their financial journeys.
To capitalize on opportunities like these, financial institutions will build AI factories that use full-stack accelerated computing to maximize performance and utilization to build AI-enabled applications that serve hundreds, if not thousands, of use cases — helping set themselves apart from the competition.
AI-assisted data governance: Due to the sensitive nature of financial data and stringent regulatory requirements, governance will be a priority for firms as they use data to create reliable and legal AI applications, including for fraud detection, predictions and forecasting, real-time calculations and customer service.
Firms will use AI models to assist in the structure, control, orchestration, processing and utilization of financial data, making the process of complying with regulations and safeguarding customer privacy smoother and less labor intensive. AI will be the key to making sense of and deriving actionable insights from the industry’s stockpile of underutilized, unstructured data.
 Richard Kerris
Richard Kerris
Vice President of Media and Entertainment
Let AI entertain you: AI will continue to revolutionize entertainment with hyperpersonalized content on every screen, from TV shows to live sports. Using generative AI and advanced vision-language models, platforms will offer immersive experiences tailored to individual tastes, interests and moods. Imagine teaser images and sizzle reels crafted to capture the essence of a new show or live event and create an instant personal connection.
In live sports, AI will enhance accessibility and cultural relevance, providing language dubbing, tailored commentary and local adaptations. AI will also elevate binge-watching by adjusting pacing, quality and engagement options in real time to keep fans captivated. This new level of interaction will transform streaming from a passive experience into an engaging journey that brings people closer to the action and each other.
AI-driven platforms will also foster meaningful connections with audiences by tailoring recommendations, trailers and content to individual preferences. AI’s hyperpersonalization will allow viewers to discover hidden gems, reconnect with old favorites and feel seen. For the industry, AI will drive growth and innovation, introducing new business models and enabling global content strategies that celebrate unique viewer preferences, making entertainment feel boundless, engaging and personally crafted.
 Ronnie Vasishta
Ronnie Vasishta
Senior Vice President of Telecoms
The AI connection: Telecommunications providers will begin to deliver generative AI applications and 5G connectivity over the same network. AI radio access network (AI-RAN) will enable telecom operators to transform traditional single-purpose base stations from cost centers into revenue-producing assets capable of providing AI inference services to devices, while more efficiently delivering the best network performance.
AI agents to the rescue: The telecommunications industry will be among the first to dial into agentic AI to perform key business functions. Telco operators will use AI agents for a wide variety of tasks, from suggesting money-saving plans to customers and troubleshooting network connectivity, to answering billing questions and processing payments.
More efficient, higher-performing networks: AI also will be used at the wireless network layer to enhance efficiency, deliver site-specific learning and reduce power consumption. Using AI as an intelligent performance improvement tool, operators will be able to continuously observe network traffic, predict congestion patterns and make adjustments before failures happen, allowing for optimal network performance.
Answering the call on sovereign AI: Nations will increasingly turn to telcos — which have proven experience managing complex, distributed technology networks — to achieve their sovereign AI objectives. The trend will spread quickly across Europe and Asia, where telcos in Switzerland, Japan, Indonesia and Norway are already partnering with national leaders to build AI factories that can use proprietary, local data to help researchers, startups, businesses and government agencies create AI applications and services.
 Xinzhou Wu
Xinzhou Wu
Vice President of Automotive
Pedal to generative AI metal: Autonomous vehicles will become more performant as developers tap into advancements in generative AI. For example, harnessing foundation models, such as vision language models, provides an opportunity to use internet-scale knowledge to solve one of the hardest problems in the autonomous vehicle (AV) field, namely that of efficiently and safely reasoning through rare corner cases.
Simulation unlocks success: More broadly, new AI-based tools will enable breakthroughs in how AV development is carried out. For example, advances in generative simulation will enable the scalable creation of complex scenarios aimed at stress-testing vehicles for safety purposes. Aside from allowing for testing unusual or dangerous conditions, simulation is also essential for generating synthetic data to enable end-to-end model training.
Three-computer approach: Effectively, new advances in AI will catalyze AV software development across the three key computers underpinning AV development — one for training the AI-based stack in the data center, another for simulation and validation, and a third in-vehicle computer to process real-time sensor data for safe driving. Together, these systems will enable continuous improvement of AV software for enhanced safety and performance of cars, trucks, robotaxis and beyond.
 Marc Spieler
Marc Spieler
Senior Managing Director of Global Energy Industry
Welcoming the smart grid: Do you know when your daily peak home electricity is? You will soon as utilities around the world embrace smart meters that use AI to broadly manage their grid networks, from big power plants and substations and, now, into the home.
As the smart grid takes shape, smart meters — once deemed too expensive to be installed in millions of homes — that combine software, sensors and accelerated computing will alert utilities when trees in a backyard brush up against power lines or when to offer big rebates to buy back the excess power stored through rooftop solar installations.
Powering up: Delivering the optimal power stack has always been mission-critical for the energy industry. In the era of generative AI, utilities will address this issue in ways that reduce environmental impact.
Expect in 2025 to see a broader embrace of nuclear power as one clean-energy path the industry will take. Demand for natural gas also will grow as it replaces coal and other forms of energy. These resurgent forms of energy are being helped by the increased use of accelerated computing, simulation technology and AI and 3D visualization, which helps optimize design, pipeline flows and storage. We’ll see the same happening at oil and gas companies, which are looking to reduce the impact of energy exploration and production.
 Azita Martin
Azita Martin
Vice President of Retail, Consumer-Packaged Goods and Quick-Service Restaurants
Software-defined retail: Supercenters and grocery stores will become software-defined, each running computer vision and sophisticated AI algorithms at the edge. The transition will accelerate checkout, optimize merchandising and reduce shrink — the industry term for a product being lost or stolen.
Each store will be connected to a headquarters AI network, using collective data to become a perpetual learning machine. Software-defined stores that continually learn from their own data will transform the shopping experience.
Intelligent supply chain: Intelligent supply chains created using digital twins, generative AI, machine learning and AI-based solvers will drive billions of dollars in labor productivity and operational efficiencies. Digital twin simulations of stores and distribution centers will optimize layouts to increase in-store sales and accelerate throughput in distribution centers.
Agentic robots working alongside associates will load and unload trucks, stock shelves and pack customer orders. Also, last-mile delivery will be enhanced with AI-based routing optimization solvers, allowing products to reach customers faster while reducing vehicle fuel costs.
]]>Austin is drawing people to jobs, music venues, comedy clubs, barbecue and more. But with this boom has come a big city blues: traffic jams.
Rekor, which offers traffic management and public safety analytics, has a front-row seat to the increasing traffic from an influx of new residents migrating to Austin. Rekor works with the Texas Department of Transportation, which has a $7 billion project addressing this, to help mitigate the roadway concerns.
“Texas has been trying to meet that growth and demand on the roadways by investing a lot in infrastructure, and they’re focusing a lot on digital infrastructure,” said Shervin Esfahani, vice president of global marketing and communications at Rekor. “It’s super complex, and they realized their traditional systems were unable to really manage and understand it in real time.”
Rekor, based in Columbia, Maryland, has been harnessing NVIDIA Metropolis for real-time video understanding and NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX modules for edge AI in Texas, Florida, Philadelphia, Georgia, Nevada, Oklahoma and many more U.S. destinations as well as in Israel and other places internationally.
Metropolis is an application framework for smart infrastructure development with vision AI. It provides developer tools, including the NVIDIA DeepStream SDK, NVIDIA TAO Toolkit, pretrained models on the NVIDIA NGC catalog and NVIDIA TensorRT. NVIDIA Jetson is a compact, powerful and energy-efficient accelerated computing platform used for embedded and robotics applications.
Rekor’s efforts in Texas and Philadelphia to help better manage roads with AI are the latest development in an ongoing story for traffic safety and traffic management.
Reducing Rubbernecking, Pileups, Fatalities and Jams
Rekor offers two main products: Rekor Command and Rekor Discover. Command is an AI-driven platform for traffic management centers, providing rapid identification of traffic events and zones of concern. It offers departments of transportation with real-time situational awareness and alerts that allows them to keep city roadways safer and more congestion-free.
Discover taps into Rekor’s edge system to fully automate the capture of comprehensive traffic and vehicle data and provides robust traffic analytics that turn roadway data into measurable, reliable traffic knowledge. With Rekor Discover, departments of transportation can see a full picture of how vehicles move on roadways and the impact they make, allowing them to better organize and execute their future city-building initiatives.
The company has deployed Command across Austin to help detect issues, analyze incidents and respond to roadway activity with a real-time view.
“For every minute an incident happens and stays on the road, it creates four minutes of traffic, which puts a strain on the road, and the likelihood of a secondary incident like an accident from rubbernecking massively goes up,” said Paul-Mathew Zamsky, vice president of strategic growth and partnerships at Rekor. “Austin deployed Rekor Command and saw a 159% increase in incident detections, and they were able to respond eight and a half minutes faster to those incidents.”
Rekor Command takes in many feeds of data — like traffic camera footage, weather, connected car info and construction updates — and taps into any other data infrastructure, as well as third-party data. It then uses AI to make connections and surface up anomalies, like a roadside incident. That information is presented in workflows to traffic management centers for review, confirmation and response.
“They look at it and respond to it, and they are doing it faster than ever before,” said Esfahani. “It helps save lives on the road, and it also helps people’s quality of life, helps them get home faster and stay out of traffic, and it reduces the strain on the system in the city of Austin.”
In addition to adopting NVIDIA’s full-stack accelerated computing for roadway intelligence, Rekor is going all in on NVIDIA AI and NVIDIA AI Blueprints, which are reference workflows for generative AI use cases, built with NVIDIA NIM microservices as part of the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform. NVIDIA NIM is a set of easy-to-use inference microservices for accelerating deployments of foundation models on any cloud or data center while keeping data secure.
Rekor has multiple large language models and vision language models running on NVIDIA Triton Inference Server in production,” according to Shai Maron, senior vice president of global software and data engineering at Rekor.
“Internally, we’ll use it for data annotation, and it will help us optimize different aspects of our day to day,” he said. “LLMs externally will help us calibrate our cameras in a much more efficient way and configure them.”
Rekor is using the NVIDIA AI Blueprint for video search and summarization to build AI agents for city services, particularly in areas such as traffic management, public safety and optimization of city infrastructure. NVIDIA recently announced a new AI Blueprint for video search and summarization enabling a range of interactive visual AI agents that extracts complex activities from massive volumes of live or archived video.
Philadelphia Monitors Roads, EV Charger Needs, Pollution
Philadelphia Navy Yard is a tourism hub run by the Philadelphia Industrial Development Corporation (PIDC), which has some challenges in road management and gathering data on new developments for the popular area. The Navy Yard location, occupying 1,200 acres, has more than 150 companies and 15,000 employees, but a $6 billion redevelopment plan there promises to bring in 12,000-plus new jobs and thousands more as residents to the area.
PIDC sought greater visibility into the effects of road closures and construction projects on mobility and how to improve mobility during significant projects and events. PIDC also looked to strengthen the Navy Yard’s ability to understand the volume and traffic flow of car carriers or other large vehicles and quantify the impact of speed-mitigating devices deployed across hazardous stretches of roadway.
Discover provided PIDC insights into additional infrastructure projects that need to be deployed to manage any changes in traffic.
Understanding the number of electric vehicles, and where they’re entering and leaving the Navy Yard, provides PIDC with clear insights on potential sites for electric vehicle (EV) charge station deployment in the future. By pulling insights from Rekor’s edge systems, built with NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX modules for powerful edge processing and AI, Rekor Discover lets Navy Yard understand the number of EVs and where they’re entering and leaving, allowing PIDC to better plan potential sites for EV charge station deployment in the future.
Rekor Discover enabled PIDC planners to create a hotspot map of EV traffic by looking at data provided by the AI platform. The solution relies on real-time traffic analysis using NVIDIA’s DeepStream data pipeline and Jetson. Additionally, it uses NVIDIA Triton Inference Server to enhance LLM capabilities.
The PIDC wanted to address public safety issues related to speeding and collisions as well as decrease property damage. Using speed insights, it’s deploying traffic calming measures where average speeds are exceeding what’s ideal on certain segments of roadway.
NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX to Monitor Pollution in Real Time
Traditionally, urban planners can look at satellite imagery to try to understand pollution locations, but Rekor’s vehicle recognition models, running on NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX modules, were able to track it to the sources, taking it a step further toward mitigation.
“It’s about air quality,” said Shobhit Jain, senior vice president of product management at Rekor. “We’ve built models to be really good at that. They can know how much pollution each vehicle is putting out.”
Looking ahead, Rekor is examining how NVIDIA Omniverse might be used for digital twins development in order to simulate traffic mitigation with different strategies. Omniverse is a platform for developing OpenUSD applications for industrial digitalization and generative physical AI.
Developing digital twins with Omniverse for municipalities has enormous implications for reducing traffic, pollution and road fatalities — all areas Rekor sees as hugely beneficial to its customers.
“Our data models are granular, and we’re definitely exploring Omniverse,” said Jain. “We’d like to see how we can support those digital use cases.”
Learn about the NVIDIA AI Blueprint for building AI agents for video search and summarization.
]]>Editor’s note: The name of NIM Agent Blueprints was changed to NVIDIA Blueprints in October 2024. All references to the name have been updated in this blog.
AI chatbots use generative AI to provide responses based on a single interaction. A person makes a query and the chatbot uses natural language processing to reply.
The next frontier of artificial intelligence is agentic AI, which uses sophisticated reasoning and iterative planning to autonomously solve complex, multi-step problems. And it’s set to enhance productivity and operations across industries.
Agentic AI systems ingest vast amounts of data from multiple sources to independently analyze challenges, develop strategies and execute tasks like supply chain optimization, cybersecurity vulnerability analysis and helping doctors with time-consuming tasks.
Agentic AI uses sophisticated reasoning and iterative planning to solve complex, multi-step problems.
How Does Agentic AI Work?
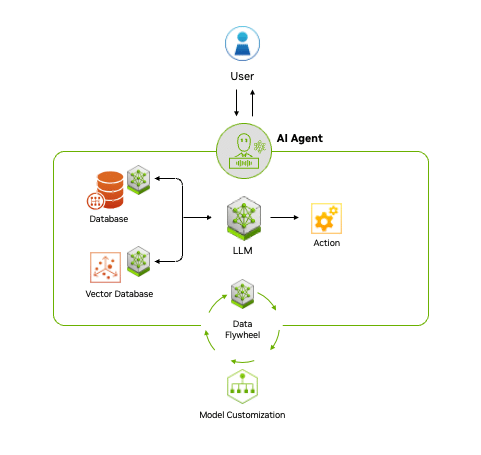
Agentic AI uses a four-step process for problem-solving:
- Perceive: AI agents gather and process data from various sources, such as sensors, databases and digital interfaces. This involves extracting meaningful features, recognizing objects or identifying relevant entities in the environment.
- Reason: A large language model acts as the orchestrator, or reasoning engine, that understands tasks, generates solutions and coordinates specialized models for specific functions like content creation, vision processing or recommendation systems. This step uses techniques like retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to access proprietary data sources and deliver accurate, relevant outputs.
- Act: By integrating with external tools and software via application programming interfaces, agentic AI can quickly execute tasks based on the plans it has formulated. Guardrails can be built into AI agents to help ensure they execute tasks correctly. For example, a customer service AI agent may be able to process claims up to a certain amount, while claims above the amount would have to be approved by a human.
- Learn: Agentic AI continuously improves through a feedback loop, or
“data flywheel,” where the data generated from its interactions is fed into the system to enhance models. This ability to adapt and become more effective over time offers businesses a powerful tool for driving better decision-making and operational efficiency.
 Fueling Agentic AI With Enterprise Data
Fueling Agentic AI With Enterprise Data
Across industries and job functions, generative AI is transforming organizations by turning vast amounts of data into actionable knowledge, helping employees work more efficiently.
AI agents build on this potential by accessing diverse data through accelerated AI query engines, which process, store and retrieve information to enhance generative AI models. A key technique for achieving this is RAG, which allows AI to tap into a broader range of data sources.
Over time, AI agents learn and improve by creating a data flywheel, where data generated through interactions is fed back into the system, refining models and increasing their effectiveness.
The end-to-end NVIDIA AI platform, including NVIDIA NeMo microservices, provides the ability to manage and access data efficiently, which is crucial for building responsive agentic AI applications.
Agentic AI in Action
The potential applications of agentic AI are vast, limited only by creativity and expertise. From simple tasks like generating and distributing content to more complex use cases such as orchestrating enterprise software, AI agents are transforming industries.
Customer Service: AI agents are improving customer support by enhancing self-service capabilities and automating routine communications. Over half of service professionals report significant improvements in customer interactions, reducing response times and boosting satisfaction.
There’s also growing interest in digital humans — AI-powered agents that embody a company’s brand and offer lifelike, real-time interactions to help sales representatives answer customer queries or solve issues directly when call volumes are high.
Content Creation: Agentic AI can help quickly create high-quality, personalized marketing content. Generative AI agents can save marketers an average of three hours per content piece, allowing them to focus on strategy and innovation. By streamlining content creation, businesses can stay competitive while improving customer engagement.
Software Engineering: AI agents are boosting developer productivity by automating repetitive coding tasks. It’s projected that by 2030 AI could automate up to 30% of work hours, freeing developers to focus on more complex challenges and drive innovation.
Healthcare: For doctors analyzing vast amounts of medical and patient data, AI agents can distill critical information to help them make better-informed care decisions. Automating administrative tasks and capturing clinical notes in patient appointments reduces the burden of time-consuming tasks, allowing doctors to focus on developing a doctor-patient connection.
AI agents can also provide 24/7 support, offering information on prescribed medication usage, appointment scheduling and reminders, and more to help patients adhere to treatment plans.
How to Get Started
With its ability to plan and interact with a wide variety of tools and software, agentic AI marks the next chapter of artificial intelligence, offering the potential to enhance productivity and revolutionize the way organizations operate.
To accelerate the adoption of generative AI-powered applications and agents, NVIDIA Blueprints provide sample applications, reference code, sample data, tools and comprehensive documentation.
NVIDIA partners including Accenture are helping enterprises use agentic AI with solutions built with NVIDIA Blueprints.
Visit ai.nvidia.com to learn more about the tools and software NVIDIA offers to help enterprises build their own AI agents.
]]>Editor’s note: The name of NIM Agent Blueprints was changed to NVIDIA Blueprints in October 2024. All references to the name have been updated in this blog.
The U.S. healthcare system is adopting digital health agents to harness AI across the board, from research laboratories to clinical settings.
The latest AI-accelerated tools — on display at the NVIDIA AI Summit taking place this week in Washington, D.C. — include NVIDIA NIM, a collection of cloud-native microservices that support AI model deployment and execution, and NVIDIA Blueprints, a catalog of pretrained, customizable workflows.
These technologies are already in use in the public sector to advance the analysis of medical images, aid the search for new therapeutics and extract information from massive PDF databases containing text, tables and graphs.
For example, researchers at the National Cancer Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), are using several AI models built with NVIDIA MONAI for medical imaging — including the VISTA-3D NIM foundation model for segmenting and annotating 3D CT images. A team at NIH’s National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) is using the NVIDIA Blueprint for generative AI-based virtual screening to reduce the time and cost of developing novel drug molecules.
With NVIDIA NIM and NVIDIA Blueprints, medical researchers across the public sector can jump-start their adoption of state-of-the-art, optimized AI models to accelerate their work. The pretrained models are customizable based on an organization’s own data and can be continually refined based on user feedback.
NIM microservices and NVIDIA Blueprints are available at ai.nvidia.com and accessible through a wide variety of cloud service providers, global system integrators and technology solutions providers.
Building With NVIDIA Blueprints
Dozens of NIM microservices and a growing set of NVIDIA Blueprints are available for developers to experience and download for free. They can be deployed in production with the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform.
- The blueprint for generative virtual screening for drug discovery brings together three NIM microservices to help researchers search and optimize libraries of small molecules to identify promising candidates that bind to a target protein.
- The multimodal PDF data extraction blueprint uses NVIDIA NeMo Retriever NIM microservices to extract insights from enterprise documents, helping developers build powerful AI agents and chatbots.
- The digital human blueprint supports the creation of interactive, AI-powered avatars for customer service. These avatars have potential applications in telehealth and nonclinical aspects of patient care, such as scheduling appointments, filling out intake forms and managing prescriptions.
Two new NIM microservices for drug discovery are now available on ai.nvidia.com to help researchers understand how proteins bind to target molecules, a crucial step in drug design. By conducting more of this preclinical research digitally, scientists can narrow down their pool of drug candidates before testing in the lab — making the discovery process more efficient and less expensive.
With the AlphaFold2-Multimer NIM microservice, researchers can accurately predict protein structure from their sequences in minutes, reducing the need for time-consuming tests in the lab. The RFdiffusion NIM microservice uses generative AI to design novel proteins that are promising drug candidates because they’re likely to bind with a target molecule.
NCATS Accelerates Drug Discovery Research
ASPIRE, a research laboratory at NCATS, is evaluating the NVIDIA Blueprint for virtual screening and is using RAPIDS, a suite of open-source software libraries for GPU-accelerated data science, to accelerate its drug discovery research. Using the cuGraph library for graph data analytics and cuDF library for accelerating data frames, the lab’s researchers can map chemical reactions across the vast unknown chemical space.
The NCATS informatics team reported that with NVIDIA AI, processes that used to take hours on CPU-based infrastructure are now done in seconds.
Massive quantities of healthcare data — including research papers, radiology reports and patient records — are unstructured and locked in PDF documents, making it difficult for researchers to quickly search for information.
The Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center, also run by NCATS, is exploring using the PDF data extraction blueprint to develop generative AI tools that enhance the center’s ability to glean information from previously unsearchable databases. These tools will help answer questions from those affected by rare diseases.
“The center analyzes data sources spanning the National Library of Medicine, the Orphanet database and other institutes and centers within the NIH to answer patient questions,” said Sam Michael, chief information officer of NCATS. “AI-powered PDF data extraction can make it massively easier to extract valuable information from previously unsearchable databases.”
Mi-NIM-al Effort, Maximum Benefit: Getting Started With NIM
A growing number of startups, cloud service providers and global systems integrators include NVIDIA NIM microservices and NVIDIA Blueprints as part of their platforms and services, making it easy for federal healthcare researchers to get started.
Abridge, an NVIDIA Inception startup and NVentures portfolio company, was recently awarded a contract from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs to help transcribe and summarize clinical appointments, reducing the burden on doctors to document each patient interaction.
The company uses NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM to accelerate AI inference and NVIDIA Triton Inference Server for deploying its audio-to-text and content summarization models at scale, some of the same technologies that power NIM microservices.
The NVIDIA Blueprint for virtual screening is now available through AWS HealthOmics, a purpose-built service that helps customers orchestrate biological data analyses.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a partner of the NIH Science and Technology Research Infrastructure for Discovery, Experimentation, and Sustainability Initiative, aka STRIDES Initiative, which aims to modernize the biomedical research ecosystem by reducing economic and process barriers to accessing commercial cloud services. NVIDIA and AWS are collaborating to make NVIDIA Blueprints broadly accessible to the biomedical research community.
ConcertAI, another NVIDIA Inception member, is an oncology AI technology company focused on research and clinical standard-of-care solutions. The company is integrating NIM microservices, NVIDIA CUDA-X microservices and the NVIDIA NeMo platform into its suite of AI solutions for large-scale clinical data processing, multi-agent models and clinical foundation models.
NVIDIA NIM microservices are supporting ConcertAI’s high-performance, low-latency AI models through its CARA AI platform. Use cases include clinical trial design, optimization and patient matching — as well as solutions that can help boost the standard of care and augment clinical decision-making.
Global systems integrator Deloitte is bringing the NVIDIA Blueprint for virtual screening to its customers worldwide. With Deloitte Atlas AI, the company can help clients at federal health agencies easily use NIM to adopt and deploy the latest generative AI pipelines for drug discovery.
Experience NVIDIA NIM microservices and NVIDIA Blueprints today.
NVIDIA AI Summit Highlights Healthcare Innovation
At the NVIDIA AI Summit in Washington, NVIDIA leaders, customers and partners are presenting over 50 sessions highlighting impactful work in the public sector.
Register for a free virtual pass to hear how healthcare researchers are accelerating innovation with NVIDIA-powered AI in these sessions:
- Federal Healthcare Leadership Panel: The Growing Importance of AI to U.S. Government Health features leaders from NVIDIA, NIH, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and more.
- Boosting U.S. Innovation and Competitiveness in AI-Enabled Healthcare and Biology features Renee Wegrzyn, director of the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health, and Rory Kelleher, global head of business development for life sciences at NVIDIA.
- Accelerated Computing Improves Translational Genomics Research features Justin Zook, coleader of the biomarker and genomic sciences group at the National Institute of Standards and Technology, and Laura Egolf, computational scientist at the National Cancer Institute’s Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research, discussing their use of NVIDIA Parabricks software for genomics research.
- Building a Specialized Interactive Foundation Model for 3D CT Segmentation features Baris Turkbey, senior clinician and head of MRI and Artificial Intelligence Resource in the National Cancer Institute’s Molecular Imaging Branch, and Pengfei Guo, applied research scientist at NVIDIA.
See notice regarding software product information.
]]>The path to safe, widespread autonomous vehicles is going digital.
MITRE — a government-sponsored nonprofit research organization — today announced its partnership with Mcity at the University of Michigan to develop a virtual and physical autonomous vehicle (AV) validation platform for industry deployment.
As part of this collaboration, announced during the NVIDIA AI Summit in Washington, D.C., MITRE will use Mcity’s simulation tools and a digital twin of its Mcity Test Facility, a real-world AV test environment in its Digital Proving Ground (DPG). The joint platform will deliver physically based sensor simulation enabled by NVIDIA Omniverse Cloud Sensor RTX APIs.
By combining these simulation capabilities with the MITRE DPG reporting framework, developers will be able to perform exhaustive testing in a simulated world to safely validate AVs before real-world deployment.
The current regulatory environment for AVs is highly fragmented, posing significant challenges for widespread deployment. Today, companies navigate regulations at various levels — city, state and the federal government — without a clear path to large-scale deployment. MITRE and Mcity aim to address this ambiguity with comprehensive validation resources open to the entire industry.
Mcity currently operates a 32-acre mock city for automakers and researchers to test their technology. Mcity is also building a digital framework around its physical proving ground to provide developers with AV data and simulation tools.
Raising Safety Standards
One of the largest gaps in the regulatory framework is the absence of universally accepted safety standards that the industry and regulators can rely on.
The lack of common standards leaves regulators with limited tools to verify AV performance and safety in a repeatable manner, while companies struggle to demonstrate the maturity of their AV technology. The ability to do so is crucial in the wake of public road incidents, where AV developers need to demonstrate the reliability of their software in a way that is acceptable to both industry and regulators.
Efforts like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration’s New Car Assessment Program (NCAP) have been instrumental in setting benchmarks for vehicle safety in traditional automotive development. However, NCAP is insufficient for AV evaluation, where measures of safety go beyond crash tests to the complexity of real-time decision-making in dynamic environments.
Additionally, traditional road testing presents inherent limitations, as it exposes vehicles to real-world conditions but lacks the scalability needed to prove safety across a wide variety of edge cases. It’s particularly difficult to test rare and dangerous scenarios on public roads without significant risk.
By providing both physical and digital resources to validate AVs, MITRE and Mcity will be able to offer a safe, universally accessible solution that addresses the complexity of verifying autonomy.
Physically Based Sensor Simulation
A core piece of this collaboration is sensor simulation, which models the physics and behavior of cameras, lidars, radars and ultrasonic sensors on a physical vehicle, as well as how these sensors interact with their surroundings.
Sensor simulation enables developers to train against and test rare and dangerous scenarios — such as extreme weather conditions, sudden pedestrian crossings or unpredictable driver behavior — safely in virtual settings.
In collaboration with regulators, AV companies can use sensor simulation to recreate a real-world event, analyze their system’s response and evaluate how their vehicle performed — accelerating the validation process.
Moreover, simulation tests are repeatable, meaning developers can track improvements or regressions in the AV stack over time. This means AV companies can provide quantitative evidence to regulators to show that their system is evolving and addressing safety concerns.
Bridging Industry and Regulators
MITRE and its ecosystem are actively developing the Digital Proving Ground platform to facilitate industry-wide standards and regulations.
The platform will be an open and accessible national resource for accelerating safe AV development and deployment, providing a trusted simulation test environment.
Mcity will contribute simulation infrastructure, a digital twin and the ability to seamlessly connect virtual and physical worlds with NVIDIA Omniverse, an open platform enabling system developers to build physical AI and robotic system simulation applications. By integrating this virtual proving ground into DPG, the collaboration will also accelerate the development and use of advanced digital engineering and simulation for AV safety assurance.
Mcity’s simulation tools will connect to Omniverse Cloud Sensor RTX APIs and render a Universal Scene Description (USD) model of Mcity’s physical proving ground. DPG will be able to access this environment, simulate the behavior of vehicles and pedestrians in a realistic test environment and use the DPG reporting framework to explain how the AV performed.
This testing will then be replicated on the physical Mcity proving ground to create a comprehensive feedback loop.
The Road Ahead
As developers, automakers and regulators continue to collaborate, the industry is moving closer to a future where AVs can operate safely and at scale. The establishment of a repeatable testbed for validating safety — across real and simulated environments — will be critical to gaining public trust and regulatory approval, bringing the promise of AVs closer to reality.
]]>Customer service departments across industries are facing increased call volumes, high customer service agent turnover, talent shortages and shifting customer expectations.
Customers expect both self-help options and real-time, person-to-person support. These expectations for seamless, personalized experiences extend across digital communication channels, including live chat, text and social media.
Despite the rise of digital channels, many consumers still prefer picking up the phone for support, placing strain on call centers. As companies strive to enhance the quality of customer interactions, operational efficiency and costs remain a significant concern.
To address these challenges, businesses are deploying AI-powered customer service software to boost agent productivity, automate customer interactions and harvest insights to optimize operations.
In nearly every industry, AI systems can help improve service delivery and customer satisfaction. Retailers are using conversational AI to help manage omnichannel customer requests, telecommunications providers are enhancing network troubleshooting, financial institutions are automating routine banking tasks, and healthcare facilities are expanding their capacity for patient care.
What Are the Benefits of AI for Customer Service?
With strategic deployment of AI, enterprises can transform customer interactions through intuitive problem-solving to build greater operational efficiencies and elevate customer satisfaction.
By harnessing customer data from support interactions, documented FAQs and other enterprise resources, businesses can develop AI tools that tap into their organization’s unique collective knowledge and experiences to deliver personalized service, product recommendations and proactive support.
Customizable, open-source generative AI technologies such as large language models (LLMs), combined with natural language processing (NLP) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), are helping industries accelerate the rollout of use-case-specific customer service AI. According to McKinsey, over 80% of customer care executives are already investing in AI or planning to do so soon.
With cost-efficient, customized AI solutions, businesses are automating management of help-desk support tickets, creating more effective self-service tools and supporting their customer service agents with AI assistants. This can significantly reduce operational costs and improve the customer experience.
Developing Effective Customer Service AI
For satisfactory, real-time interactions, AI-powered customer service software must return accurate, fast and relevant responses. Some tricks of the trade include:
Open-source foundation models can fast-track AI development. Developers can flexibly adapt and enhance these pretrained machine learning models, and enterprises can use them to launch AI projects without the high costs of building models from scratch.
RAG frameworks connect foundation or general-purpose LLMs to proprietary knowledge bases and data sources, including inventory management and customer relationship management systems and customer service protocols. Integrating RAG into conversational chatbots, AI assistants and copilots tailors responses to the context of customer queries.
Human-in-the-loop processes remain crucial to both AI training and live deployments. After initial training of foundation models or LLMs, human reviewers should judge the AI’s responses and provide corrective feedback. This helps to guard against issues such as hallucination — where the model generates false or misleading information, and other errors including toxicity or off-topic responses. This type of human involvement ensures fairness, accuracy and security is fully considered during AI development.
Human participation is even more important for AI in production. When an AI is unable to adequately resolve a customer question, the program must be able to route the call to customer support teams. This collaborative approach between AI and human agents ensures that customer engagement is efficient and empathetic.
What’s the ROI of Customer Service AI?
The return on investment of customer service AI should be measured primarily based on efficiency gains and cost reductions. To quantify ROI, businesses can measure key indicators such as reduced response times, decreased operational costs of contact centers, improved customer satisfaction scores and revenue growth resulting from AI-enhanced services.
For instance, the cost of implementing an AI chatbot using open-source models can be compared with the expenses incurred by routing customer inquiries through traditional call centers. Establishing this baseline helps assess the financial impact of AI deployments on customer service operations.
To solidify understanding of ROI before scaling AI deployments, companies can consider a pilot period. For example, by redirecting 20% of call center traffic to AI solutions for one or two quarters and closely monitoring the outcomes, businesses can obtain concrete data on performance improvements and cost savings. This approach helps prove ROI and informs decisions for further investment.
Businesses across industries are using AI for customer service and measuring their success:
Retailers Reduce Call Center Load
Modern shoppers expect smooth, personalized and efficient shopping experiences, whether in store or on an e-commerce site. Customers of all generations continue prioritizing live human support, while also desiring the option to use different channels. But complex customer issues coming from a diverse customer base can make it difficult for support agents to quickly comprehend and resolve incoming requests.
To address these challenges, many retailers are turning to conversational AI and AI-based call routing. According to NVIDIA’s 2024 State of AI in Retail and CPG report, nearly 70% of retailers believe that AI has already boosted their annual revenue.
CP All, Thailand’s sole licensed operator for 7-Eleven convenience stores, has implemented conversational AI chatbots in its call centers, which rack up more than 250,000 calls per day. Training the bots presented unique challenges due to the complexities of the Thai language, which includes 21 consonants, 18 pure vowels, three diphthongs and five tones.
To manage this, CP All used NVIDIA NeMo, a framework designed for building, training and fine-tuning GPU-accelerated speech and natural language understanding models. With automatic speech recognition and NLP models powered by NVIDIA technologies, CP All’s chatbot achieved a 97% accuracy rate in understanding spoken Thai.
With the conversational chatbot handling a significant number of customer conversations, the call load on human agents was reduced by 60%. This allowed customer service teams to focus on more complex tasks. The chatbot also helped reduce wait times and provided quicker, more accurate responses, leading to higher customer satisfaction levels.
With AI-powered support experiences, retailers can enhance customer retention, strengthen brand loyalty and boost sales.
Telecommunications Providers Automate Network Troubleshooting
Telecommunications providers are challenged to address complex network issues while adhering to service-level agreements with end customers for network uptime. Maintaining network performance requires rapid troubleshooting of network devices, pinpointing root causes and resolving difficulties at network operations centers.
With its abilities to analyze vast amounts of data, troubleshoot network problems autonomously and execute numerous tasks simultaneously, generative AI is ideal for network operations centers. According to an IDC survey, 73% of global telcos have prioritized AI and machine learning investments for operational support as their top transformation initiative, underscoring the industry’s shift toward AI and advanced technologies.
Infosys, a leader in next-generation digital services and consulting, has built AI-driven solutions to help its telco partners overcome customer service challenges. Using NVIDIA NIM microservices and RAG, Infosys developed an AI chatbot to support network troubleshooting.
By offering quick access to essential, vendor-agnostic router commands for diagnostics and monitoring, the generative AI-powered chatbot significantly reduces network resolution times, enhancing overall customer support experiences.
To ensure accuracy and contextual responses, Infosys trained the generative AI solution on telecom device-specific manuals, training documents and troubleshooting guides. Using NVIDIA NeMo Retriever to query enterprise data, Infosys achieved 90% accuracy for its LLM output. By fine-tuning and deploying models with NVIDIA technologies, Infosys achieved a latency of 0.9 seconds, a 61% reduction compared with its baseline model. The RAG-enabled chatbot powered by NeMo Retriever also attained 92% accuracy, compared with the baseline model’s 85%.
With AI tools supporting network administrators, IT teams and customer service agents, telecom providers can more efficiently identify and resolve network issues.
Financial Services Institutions Pinpoint Fraud With Ease
While customers expect anytime, anywhere banking and support, financial services require a heightened level of data sensitivity. And unlike other industries that may include one-off purchases, banking is typically based on ongoing transactions and long-term customer relationships.
At the same time, user loyalty can be fleeting, with up to 80% of banking customers willing to switch institutions for a better experience. Financial institutions must continuously improve their support experiences and update their analyses of customer needs and preferences.
Many banks are turning to AI virtual assistants that can interact directly with customers to manage inquiries, execute transactions and escalate complex issues to human customer support agents. According to NVIDIA’s 2024 State of AI in Financial Services report, more than one-fourth of survey respondents are using AI to enhance customer experiences, and 34% are exploring the use of generative AI and LLMs for customer experience and engagement.
Bunq, a European digital bank with more than 2 million customers and 8 billion euros worth of deposits, is deploying generative AI to meet user needs. With proprietary LLMs, the company built Finn, a personal AI assistant available to both customers and bank employees. Finn can answer finance-related inquiries such as “How much did I spend on groceries last month?” or “What is the name of the Indian restaurant I ate at last week?”
Plus, with a human-in-the-loop process, Finn helps employees more quickly identify fraud. By collecting and analyzing data for compliance officers to review, bunq now identifies fraud in just three to seven minutes, down from 30 minutes without Finn.
By deploying AI tools that can use data to protect customer transactions, execute banking requests and act on customer feedback, financial institutions can serve customers at a higher level, building the trust and satisfaction necessary for long-term relationships.
Healthcare and Life Sciences Organizations Overcome Staffing Shortages
In healthcare, patients need quick access to medical expertise, precise and tailored treatment options, and empathetic interactions with healthcare professionals. But with the World Health Organization estimating a 10 million personnel shortage by 2030, access to quality care could be jeopardized.
AI-powered digital healthcare assistants are helping medical institutions do more with less. With LLMs trained on specialized medical corpuses, AI copilots can save physicians and nurses hours of daily work by helping with clinical note-taking, automating order-placing for prescriptions and lab tests, and following up with after-visit patient notes.
Multimodal AI that combines language and vision models can make healthcare settings safer by extracting insights and providing summaries of image data for patient monitoring. For example, such technology can alert staff of patient fall risks and other patient room hazards.
To support healthcare professionals, Hippocratic AI has trained a generative AI healthcare agent to perform low-risk, non-diagnostic routine tasks, like reminding patients of necessary appointment prep and following up after visits to make sure medication routines are being followed and no adverse side effects are being experienced.
Hippocratic AI trained its models on evidence-based medicine and completed rigorous testing with a large group of certified nurses and doctors. The constellation architecture of the solution comprises 20 models, one of which communicates with patients while the other 19 supervise its output. The complete system contains 1.7 trillion parameters.
The possibility of every doctor and patient having their own AI-powered digital healthcare assistant means reduced clinician burnout and higher-quality medical care.
Raising the Bar for Customer Experiences With AI
By integrating AI into customer service interactions, businesses can offer more personalized, efficient and prompt service, setting new standards for omnichannel support experiences across platforms. With AI virtual assistants that process vast amounts of data in seconds, enterprises can equip their support agents to deliver tailored responses to the complex needs of a diverse customer base.
To develop and deploy effective customer service AI, businesses can fine-tune AI models and deploy RAG solutions to meet diverse and specific needs.
NVIDIA offers a suite of tools and technologies to help enterprises get started with customer service AI.
NVIDIA NIM microservices, part of the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform, accelerate generative AI deployment and support various optimized AI models for seamless, scalable inference. NVIDIA NIM Agent Blueprints provide developers with packaged reference examples to build innovative solutions for customer service applications.
By taking advantage of AI development tools, enterprises can build accurate and high-speed AI applications to transform employee and customer experiences.
Learn more about improving customer service with generative AI.
]]>Editor’s note: This post is part of the AI Decoded series, which demystifies AI by making the technology more accessible, and showcases new hardware, software, tools and accelerations for RTX PC users.
AI powered by NVIDIA GPUs is accelerating nearly every industry, creating high demand for graduates, especially from STEM fields, who are proficient in using the technology. Millions of students worldwide are participating in university STEM programs to learn skills that will set them up for career success.
To prepare students for the future job market, NVIDIA has worked with top universities to develop a GPU-accelerated AI curriculum that’s now taught in more than 5,000 schools globally. Students can get a jumpstart outside of class with NVIDIA’s AI Learning Essentials, a set of resources that equips individuals with the necessary knowledge, skills and certifications for the rapidly evolving AI workforce.
NVIDIA GPUs — whether running in university data centers, GeForce RTX laptops or NVIDIA RTX workstations — are accelerating studies, helping enhance the learning experience and enabling students to gain hands-on experience with hardware used widely in real-world applications.
Supercharged AI Studies
NVIDIA provides several tools to help students accelerate their studies.
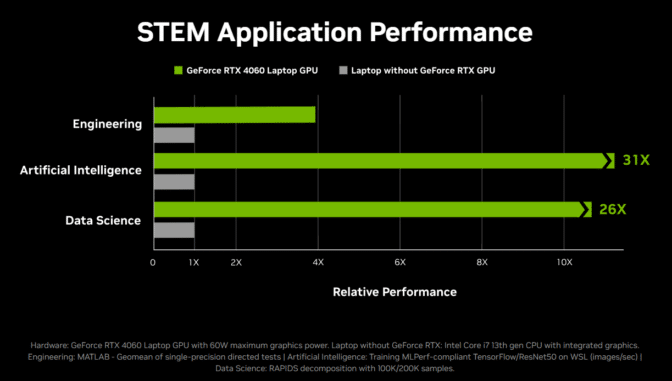
The RTX AI Toolkit is a powerful resource for students looking to develop and customize AI models for projects in computer science, data science, and other STEM fields. It allows students to train and fine-tune the latest generative AI models, including Gemma, Llama 3 and Phi 3, up to 30x faster — enabling them to iterate and innovate more efficiently, advancing their studies and research projects.
Students studying data science and economics can use NVIDIA RAPIDS AI and data science software libraries to run traditional machine learning models up to 25x faster than conventional methods, helping them handle large datasets more efficiently, perform complex analyses in record time and gain deeper insights from data.
AI-deal for Robotics, Architecture and Design
Students studying robotics can tap the NVIDIA Isaac platform for developing, testing and deploying AI-powered robotics applications. Powered by NVIDIA GPUs, the platform consists of NVIDIA-accelerated libraries, applications frameworks and AI models that supercharge the development of AI-powered robots like autonomous mobile robots, arms and manipulators, and humanoids.
While GPUs have long been used for 3D design, modeling and simulation, their role has significantly expanded with the advancement of AI. GPUs are today used to run AI models that dramatically accelerate rendering processes.
Some industry-standard design tools powered by NVIDIA GPUs and AI include:
- SOLIDWORKS Visualize: This 3D computer-aided design rendering software uses NVIDIA Optix AI-powered denoising to produce high-quality ray-traced visuals, streamlining the design process by providing faster, more accurate visual feedback.
- Blender: This popular 3D creation suite uses NVIDIA Optix AI-powered denoising to deliver stunning ray-traced visuals, significantly accelerating content creation workflows.
- D5 Render: Commonly used by architects, interior designers and engineers, D5 Render incorporates NVIDIA DLSS technology for real-time viewport rendering, enabling smoother, more detailed visualizations without sacrificing performance. Powered by fourth-generation Tensor Cores and the NVIDIA Optical Flow Accelerator on GeForce RTX 40 Series GPUs and NVIDIA RTX Ada Generation GPUs, DLSS uses AI to create additional frames and improve image quality.
- Enscape: Enscape makes it possible to ray trace more geometry at a higher resolution, at exactly the same frame rate. It uses DLSS to enhance real-time rendering capabilities, providing architects and designers with seamless, high-fidelity visual previews of their projects.
Beyond STEM
Students, hobbyists and aspiring artists use the NVIDIA Studio platform to supercharge their creative processes with RTX and AI. RTX GPUs power creative apps such as Adobe Creative Cloud, Autodesk, Unity and more, accelerating a variety of processes such as exporting videos and rendering art.
ChatRTX is a demo app that lets students create a personalized GPT large language model connected to their own content and study materials, including text, images or other data. Powered by advanced AI, ChatRTX functions like a personalized chatbot that can quickly provide students relevant answers to questions based on their connected content. The app runs locally on a Windows RTX PC or workstation, meaning students can get fast, secure results personalized to their needs.
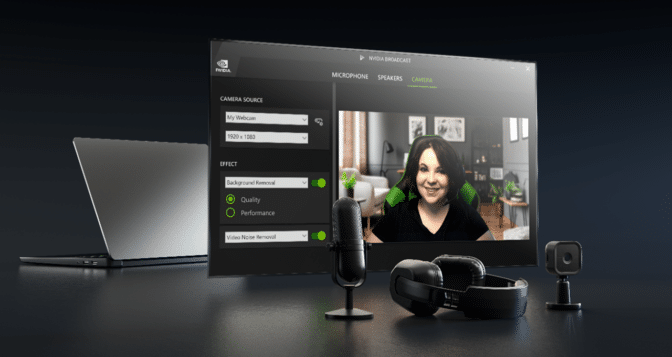
Schools are increasingly adopting remote learning as a teaching modality. NVIDIA Broadcast — a free application that delivers professional-level audio and video with AI-powered features on RTX PCs and workstations — integrates seamlessly with remote learning applications including BlueJeans, Discord, Google Meet, Microsoft Teams, Webex and Zoom. It uses AI to enhance remote learning experiences by removing background noise, improving image quality in low-light scenarios, and enabling background blur and background replacement.
From Data Centers to School Laptops
NVIDIA RTX-powered mobile workstations and GeForce RTX and Studio RTX 40 Series laptops offer supercharged development, learning, gaming and creating experiences with AI-enabled tools and apps. They also include exclusive access to the NVIDIA Studio platform of creative tools and technologies, and Max-Q technologies that optimize battery life and acoustics — giving students an ideal platform for all aspects of campus life.
Say goodbye to late nights in the computer lab — GeForce RTX laptops and NVIDIA RTX workstations share the same architecture as the NVIDIA GPUs powering many university labs and data centers. That means students can study, create and play — all on the same PC.
Learn more about GeForce RTX laptops and NVIDIA RTX workstations.
]]>Generative AI is unlocking new ways for enterprises to engage customers through digital human avatars.
At SIGGRAPH, NVIDIA previewed “James,” an interactive digital human that can connect with people using emotions, humor and more. James is based on a customer-service workflow using NVIDIA ACE, a reference design for creating custom, hyperrealistic, interactive avatars.
Users can interact with James in real time at ai.nvidia.com.
NVIDIA also showcased at the computer graphics conference the latest advancements to the NVIDIA Maxine AI platform, including Maxine 3D and Audio2Face-2D for an immersive telepresence experience.
Developers can use Maxine and NVIDIA ACE digital human technologies to make customer interactions with digital interfaces more engaging and natural. ACE technologies enable digital human development with AI models for speech and translation, vision, intelligence, lifelike animation and behavior, and realistic appearance.
Companies across industries are using Maxine and ACE to deliver immersive virtual customer experiences.
Meet James, a Digital Brand Ambassador
Built on top of NVIDIA NIM microservices, James is a virtual assistant that can provide contextually accurate responses.
Using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), James can accurately tell users about the latest NVIDIA technologies. ACE allows developers to use their own data to create domain-specific avatars that can communicate relevant information to customers.
James is powered by the latest NVIDIA RTX rendering technologies for advanced, lifelike animations. His natural-sounding voice is powered by ElevenLabs. NVIDIA ACE lets developers customize animation, voice and language when building avatars tailored for different use cases.
NVIDIA Maxine Enhances Digital Humans in Telepresence
Maxine, a platform for deploying cutting-edge AI features that enhance the audio and video quality of digital humans, enables the use of real-time, photorealistic 2D and 3D avatars with video-conferencing devices.
Maxine 3D converts 2D video portrait inputs into 3D avatars, allowing the integration of highly realistic digital humans in video conferencing and other two-way communication applications. The technology will soon be available in early access.
Audio2Face-2D, currently in early access, animates static portraits based on audio input, creating dynamic, speaking digital humans from a single image. Try the technology at ai.nvidia.com.
Companies Embracing Digital Human Applications
HTC, Looking Glass, Reply and UneeQ are among the latest companies using NVIDIA ACE and Maxine across a broad range of use cases, including customer service agents, and telepresence experiences in entertainment, retail and hospitality.
At SIGGRAPH, digital human technology developer UneeQ is showcasing two new demos.
The first spotlights cloud-rendered digital humans powered by NVIDIA GPUs with local, in-browser computer vision for enhanced scalability and privacy, and animated using the Audio2Face-3D NVIDIA NIM microservice. UneeQ’s Synapse technology processes anonymized user data and feeds it to a large language model (LLM) for more accurate, responsive interactions.
The second demo runs on a single NVIDIA RTX GPU-powered laptop, featuring an advanced digital human powered by Gemma 7B LLM, RAG and the NVIDIA Audio2Face-3D NIM microservice.
Both demos showcase UneeQ’s NVIDIA-powered efforts to develop digital humans that can react to users’ facial expressions and actions, pushing the boundaries of realism in virtual customer service experiences.
HTC Viverse has integrated the Audio2Face-3D NVIDIA NIM microservice into its VIVERSE AI agent for dynamic facial animation and lip sync, allowing for more natural and immersive user interactions.
Hologram technology company Looking Glass’ Magic Mirror demo at SIGGRAPH uses a simple camera setup and Maxine’s advanced 3D AI capabilities to generate a real-time holographic feed of users’ faces on its newly launched, group-viewable Looking Glass 16-inch and 32-inch Spatial Displays.
Reply is unveiling an enhanced version of Futura, its cutting-edge digital human developed for Costa Crociere’s Costa Smeralda cruise ship. Powered by Audio2Face-3D NVIDIA NIM and Riva ASR NIM microservices, Futura’s speech-synthesis capabilities tap advanced technologies including GPT-4o, LlamaIndex for RAG and Microsoft Azure text-to-speech services.
Futura also incorporates Reply’s proprietary affective computing technology, alongside Hume AI and MorphCast, for comprehensive emotion recognition. Built using Unreal Engine 5.4.3 and MetaHuman Creator with NVIDIA ACE-powered facial animation, Futura supports six languages. The intelligent assistant can help plan personalized port visits, suggest tailored itineraries and facilitate tour bookings.
In addition, Futura refines recommendations based on guest feedback and uses a specially created knowledge base to provide informative city presentations, enhancing tourist itineraries. Futura aims to enhance customer service and offer immersive interactions in real-world scenarios, leading to streamlined operations and driving business growth.
Learn more about NVIDIA ACE and NVIDIA Maxine.
Discover how accelerated computing and generative AI are transforming industries and creating new opportunities for innovation by watching NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang’s fireside chats at SIGGRAPH.
See notice regarding software product information.
]]>Editor’s note: This post is part of our In the NVIDIA Studio series, which celebrates featured artists, offers creative tips and tricks, and demonstrates how NVIDIA Studio technology improves creative workflows. We’re also deep diving on new GeForce RTX GPU features, technologies and resources, and how they dramatically accelerate content creation.
Wondershare Filmora — a video editing app with AI-powered tools — now supports NVIDIA RTX Video HDR, joining editing software like Blackmagic Design’s DaVinci Resolve and Cyberlink PowerDirector.
RTX Video HDR significantly enhances video quality, ensuring the final output is suitable for the best monitors available today.
Livestreaming software OBS Studio and XSplit Broadcaster now support Twitch Enhanced Broadcasting, giving streamers more control over video quality through client-side encoding and automatic configurations. The feature, developed in collaboration between Twitch, OBS and NVIDIA, also paves the way for more advancements, including vertical live video and advanced codecs such as HEVC and AV1.
A summer’s worth of creative app updates are included in the July Studio Driver, ready for download today. Install the NVIDIA app beta — the essential companion for creators and gamers — to keep GeForce RTX PCs up to date with the latest NVIDIA drivers and technology.
Join NVIDIA at SIGGRAPH to learn about the latest breakthroughs in graphics and generative AI, and tune in to a fireside chat featuring NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang and Lauren Goode, senior writer at WIRED, on Monday, July 29 at 2:30 p.m. MT. Register now.
And this week’s featured In the NVIDIA Studio artist, Kevin Stratvert, shares all about AI-powered content creation in Wondershare Filmora.
(Wonder)share the Beauty of RTX Video
RTX Video HDR analyzes standard dynamic range video and transforms it into HDR10-quality video, expanding the color gamut to produce clearer, more vibrant frames and enhancing the sense of depth for greater immersion.
With RTX Video HDR, Filmora users can create high-quality content that’s ideal for gaming videos, travel vlogs or event filmmaking.
Combining RTX Video HDR with RTX Video Super Resolution — another AI-powered tool that uses trained models to sharpen edges, restore features and remove artifacts in video — further enhances visual quality. RTX Video HDR requires an NVIDIA RTX GPU connected to an HDR10-compatible monitor or TV. For more information, check out the RTX Video FAQ.
Those with a RTX GPU-powered PC can send files to the Filmora desktop app and continue to edit with local RTX acceleration, doubling the speed of the export process with dual encoders on GeForce RTX 4070 Ti or above GPUs.
Learn more about Wondershare Filmora’s AI-powered features.
Maximizing AI Features in Filmora
Kevin Stratvert has the heart of a teacher — he’s always loved to share his technical knowledge and tips with others.
One day, he thought, “Why not make a YouTube video to explain stuff directly to users?” His first big hit was a tutorial on how to get Microsoft Office for free through Office.com. The video garnered millions of views and tons of engagement — and he’s continued creating content ever since.
“The more content I created, the more questions and feedback I got from viewers, sparking this cycle of creativity and connection that I just couldn’t get enough of,” said Stratvert.
Explaining the benefits of AI has been an area of particular interest for Stratvert, especially as it relates to AI-powered features in Wondershare Filmora. In one YouTube video, Filmora Video Editor Tutorial for Beginners, he breaks down the AI effects video editors can use to accelerate their workflows.
Examples include:
- Smart Edit: Edit footage-based transcripts generated automatically, including in multiple languages.
- Smart Cutout: Remove unwanted objects or change the background in seconds.
- Speech-to-Text: Automatically generate compelling descriptions, titles and captions.
“AI has become a crucial part of my creative toolkit, especially for refining details that really make a difference,” said Stratvert. “By handling these technical tasks, AI frees up my time to focus more on creating content, making the whole process smoother and more efficient.”
Stratvert has also been experimenting with NVIDIA ChatRTX, a technology that lets users interact with their local data, installing and configuring various AI models, effectively prompting AI for both text and image outputs using CLIP and more.
NVIDIA Broadcast has been instrumental in giving Stratvert a professional setup for web conferences and livestreams. The app’s features, including background noise removal and virtual background, help maintain a professional appearance on screen. It’s especially useful in home studio settings, where controlling variables in the environment can be challenging.
“NVIDIA Broadcast has been instrumental in professionalizing my setup for web conferences and livestreams.” — Kevin Stratvert
Stratvert stresses the importance of his GeForce RTX 4070 graphics card in the content creation process.
“With an RTX GPU, I’ve noticed a dramatic improvement in render times and the smoothness of playback, even in demanding scenarios,” he said. “Additionally, the advanced capabilities of RTX GPUs support more intensive tasks like real-time ray tracing and AI-driven editing features, which can open up new creative possibilities in my edits.”
Check out Stratvert’s video tutorials on his website.

Follow NVIDIA Studio on Instagram, X and Facebook. Access tutorials on the Studio YouTube channel and get updates directly in your inbox by subscribing to the Studio newsletter.
]]>Sphere, a new kind of entertainment medium in Las Vegas, is joining the ranks of legendary circular performance spaces such as the Roman Colosseum and Shakespeare’s Globe Theater — captivating audiences with eye-popping LED displays that cover nearly 750,000 square feet inside and outside the venue.
Behind the screens, around 150 NVIDIA RTX A6000 GPUs help power stunning visuals on floor-to-ceiling, 16x16K displays across the Sphere’s interior, as well as 1.2 million programmable LED pucks on the venue’s exterior — the Exosphere, which is the world’s largest LED screen.
Delivering robust network connectivity, NVIDIA BlueField DPUs and NVIDIA ConnectX-6 Dx NICs — along with the NVIDIA DOCA Firefly Service and NVIDIA Rivermax software for media streaming — ensure that all the display panels act as one synchronized canvas.
“Sphere is captivating audiences not only in Las Vegas, but also around the world on social media, with immersive LED content delivered at a scale and clarity that has never been done before,” said Alex Luthwaite, senior vice president of show systems technology at Sphere Entertainment. “This would not be possible without the expertise and innovation of companies such as NVIDIA that are critical to helping power our vision, working closely with our team to redefine what is possible with cutting-edge display technology.”
Named one of TIME’s Best Inventions of 2023, Sphere hosts original Sphere Experiences, concerts and residencies from the world’s biggest artists, and premier marquee and corporate events.
Rock band U2 opened Sphere with a 40-show run that concluded in March. Other shows include The Sphere Experience featuring Darren Aronofsky’s Postcard From Earth, a specially created multisensory cinematic experience that showcases all of the venue’s immersive technologies, including high-resolution visuals, advanced concert-grade sound, haptic seats and atmospheric effects such as wind and scents.

Behind the Screens: Visual Technology Fueling the Sphere
Sphere Studios creates video content in its Burbank, Calif., facility, then transfers it digitally to Sphere in Las Vegas. The content is then streamed in real time to rack-mounted workstations equipped with NVIDIA RTX A6000 GPUs, achieving unprecedented performance capable of delivering three layers of 16K resolution at 60 frames per second.
The NVIDIA Rivermax software helps provide media streaming acceleration, enabling direct data transfers to and from the GPU. Combined, the software and hardware acceleration eliminates jitter and optimizes latency.
NVIDIA BlueField DPUs also facilitate precision timing through the DOCA Firefly Service, which is used to synchronize clocks in a network with sub-microsecond accuracy.
“The integration of NVIDIA RTX GPUs, BlueField DPUs and Rivermax software creates a powerful trifecta of advantages for modern accelerated computing, supporting the unique high-resolution video streams and strict timing requirements needed at Sphere and setting a new standard for media processing capabilities,” said Nir Nitzani, senior product director for networking software at NVIDIA. “This collaboration results in remarkable performance gains, culminating in the extraordinary experiences guests have at Sphere.”
Well-Rounded: From Simulation to Sphere Stage
To create new immersive content exclusively for Sphere, Sphere Entertainment launched Sphere Studios, which is dedicated to developing the next generation of original immersive entertainment. The Burbank campus consists of numerous development facilities, including a quarter-sized version of Sphere screen in Las Vegas, dubbed Big Dome, which serves as a specialized screening, production facility and lab for content.

Sphere Studios also developed the Big Sky camera system, which captures uncompressed, 18K images from a single camera, so that the studio can film content for Sphere without needing to stitch multiple camera feeds together. The studio’s custom image processing software runs on Lenovo servers powered by NVIDIA A40 GPUs.
The A40 GPUs also fuel creative work, including 3D video, virtualization and ray tracing. To develop visuals for different kinds of shows, the team works with apps including Unreal Engine, Unity, Touch Designer and Notch.
For more, explore upcoming sessions in NVIDIA’s room at SIGGRAPH and watch the panel discussion “Immersion in Sphere: Redefining Live Entertainment Experiences” on NVIDIA On-Demand.
All images courtesy of Sphere Entertainment.
]]>Generative AI has revolutionized software development with prompt-based code generation — protein design is next.
EvolutionaryScale today announced the release of its ESM3 model, the third-generation ESM model, which simultaneously reasons over the sequence, structure and functions of proteins, giving protein discovery engineers a programmable platform.
The startup, which emerged from the Meta FAIR (Fundamental AI Research) unit, recently landed funding led by Lux Capital, Nat Friedman and Daniel Gross, with investment from NVIDIA and Amazon.
At the forefront of programmable biology, EvolutionaryScale can assist researchers in engineering proteins that can help target cancer cells, find alternatives to harmful plastics, drive environmental mitigations and more.
EvolutionaryScale is pioneering the frontier of programmable biology with the scale-out model development of ESM3, which used NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs for the most compute ever put into a biological foundation model. The 98 billion parameter ESM3 model uses roughly 25x more flops and 60x more data than its predecessor, ESM2.
The company, which developed a database of more than 2 billion protein sequences to train its AI model, offers technology that can provide clues applicable to drug development, disease eradication and, literally, how humans have evolved at scale as a species — as its name suggests — for drug discovery researchers.
Accelerating In Silico Biological Research With ESM3
With leaps in training data, EvolutionaryScale aims to accelerate protein discovery with ESM3.
The model was trained on almost 2.8 billion protein sequences sampled from organisms and biomes, allowing scientists to prompt the model to identify and validate new proteins with increasing levels of accuracy.
ESM3 offers significant updates over previous versions. The model is natively generative, and it is an “all to all” model, meaning structure and function annotations can be provided as input rather than just as output.
Once it’s made publicly available, scientists can fine-tune this base model to construct purpose-built models based on their own proprietary data. The boost in protein engineering capabilities due to ESM3’s large-scale generative training across enormous amounts of data offers a time-traveling machine for in silico biological research.
Driving the Next Big Breakthroughs With NVIDIA BioNeMo
ESM3 provides biologists and protein designers with a generative AI boost, helping improve their engineering and understanding of proteins. With simple prompts, it can generate new proteins with a provided scaffold, self-improve its protein design based on feedback and design proteins based on the functionality that the user indicates. These capabilities can be used in tandem in any combination to provide chain-of-thought protein design as if the user were messaging a researcher who had memorized the intricate three-dimensional meaning of every protein sequence known to humans and had learned the language fluently, enabling users to iterate back and forth.
“In our internal testing we’ve been impressed by the ability of ESM3 to creatively respond to a variety of complex prompts,” said Tom Sercu, co-founder and VP of engineering at EvolutionaryScale. “It was able to solve an extremely hard protein design problem to create a novel Green Fluorescent Protein. We expect ESM3 will help scientists accelerate their work and open up new possibilities — we’re looking forward to seeing how it will contribute to future research in the life sciences.”
EvolutionaryScale will be opening an API for closed beta today and code and weights are available for a small open version of ESM3 for non-commercial use. This version is coming soon to NVIDIA BioNeMo, a generative AI platform for drug discovery. The full ESM3 family of models will soon be available to select customers as an NVIDIA NIM microservice, run-time optimized in collaboration with NVIDIA, and supported by an NVIDIA AI Enterprise software license for testing at ai.nvidia.com.
The computing power required to train these models is growing exponentially. ESM3 was trained using the Andromeda cluster, which uses NVIDIA H100 GPUs and NVIDIA Quantum-2 InfiniBand networking.
The ESM3 model will be available on select partner platforms, including Amazon Bedrock, Amazon Sagemaker, AWS HealthOMICs and NVIDIA BioNeMo.
See notice regarding software product information.
]]>NVIDIA contributed the largest ever indoor synthetic dataset to the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) conference’s annual AI City Challenge — helping researchers and developers advance the development of solutions for smart cities and industrial automation.
The challenge, garnering over 700 teams from nearly 50 countries, tasks participants to develop AI models to enhance operational efficiency in physical settings, such as retail and warehouse environments, and intelligent traffic systems.
Teams tested their models on the datasets that were generated using NVIDIA Omniverse, a platform of application programming interfaces (APIs), software development kits (SDKs) and services that enable developers to build Universal Scene Description (OpenUSD)-based applications and workflows.
Creating and Simulating Digital Twins for Large Spaces
In large indoor spaces like factories and warehouses, daily activities involve a steady stream of people, small vehicles and future autonomous robots. Developers need solutions that can observe and measure activities, optimize operational efficiency, and prioritize human safety in complex, large-scale settings.
Researchers are addressing that need with computer vision models that can perceive and understand the physical world. It can be used in applications like multi-camera tracking, in which a model tracks multiple entities within a given environment.
To ensure their accuracy, the models must be trained on large, ground-truth datasets for a variety of real-world scenarios. But collecting that data can be a challenging, time-consuming and costly process.
AI researchers are turning to physically based simulations — such as digital twins of the physical world — to enhance AI simulation and training. These virtual environments can help generate synthetic data used to train AI models. Simulation also provides a way to run a multitude of “what-if” scenarios in a safe environment while addressing privacy and AI bias issues.
Creating synthetic data is important for AI training because it offers a large, scalable, and expandable amount of data. Teams can generate a diverse set of training data by changing many parameters including lighting, object locations, textures and colors.
Building Synthetic Datasets for the AI City Challenge
This year’s AI City Challenge consists of five computer vision challenge tracks that span traffic management to worker safety.
NVIDIA contributed datasets for the first track, Multi-Camera Person Tracking, which saw the highest participation, with over 400 teams. The challenge used a benchmark and the largest synthetic dataset of its kind — comprising 212 hours of 1080p videos at 30 frames per second spanning 90 scenes across six virtual environments, including a warehouse, retail store and hospital.
Created in Omniverse, these scenes simulated nearly 1,000 cameras and featured around 2,500 digital human characters. It also provided a way for the researchers to generate data of the right size and fidelity to achieve the desired outcomes.
The benchmarks were created using Omniverse Replicator in NVIDIA Isaac Sim, a reference application that enables developers to design, simulate and train AI for robots, smart spaces or autonomous machines in physically based virtual environments built on NVIDIA Omniverse.
Omniverse Replicator, an SDK for building synthetic data generation pipelines, automated many manual tasks involved in generating quality synthetic data, including domain randomization, camera placement and calibration, character movement, and semantic labeling of data and ground-truth for benchmarking.
Ten institutions and organizations are collaborating with NVIDIA for the AI City Challenge:
- Australian National University, Australia
- Emirates Center for Mobility Research, UAE
- Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, India
- Iowa State University, U.S.
- Johns Hopkins University, U.S.
- National Yung-Ming Chiao-Tung University, Taiwan
- Santa Clara University, U.S.
- The United Arab Emirates University, UAE
- University at Albany – SUNY, U.S.
- Woven by Toyota, Japan
Driving the Future of Generative Physical AI
Researchers and companies around the world are developing infrastructure automation and robots powered by physical AI — which are models that can understand instructions and autonomously perform complex tasks in the real world.
Generative physical AI uses reinforcement learning in simulated environments, where it perceives the world using accurately simulated sensors, performs actions grounded by laws of physics, and receives feedback to reason about the next set of actions.
Developers can tap into developer SDKs and APIs, such as the NVIDIA Metropolis developer stack — which includes a multi-camera tracking reference workflow — to add enhanced perception capabilities for factories, warehouses and retail operations. And with the latest release of NVIDIA Isaac Sim, developers can supercharge robotics workflows by simulating and training AI-based robots in physically based virtual spaces before real-world deployment.
Researchers and developers are also combining high-fidelity, physics-based simulation with advanced AI to bridge the gap between simulated training and real-world application. This helps ensure that synthetic training environments closely mimic real-world conditions for more seamless robot deployment.
NVIDIA is taking the accuracy and scale of simulations further with the recently announced NVIDIA Omniverse Cloud Sensor RTX, a set of microservices that enable physically accurate sensor simulation to accelerate the development of fully autonomous machines.
This technology will allow autonomous systems, whether a factory, vehicle or robot, to gather essential data to effectively perceive, navigate and interact with the real world. Using these microservices, developers can run large-scale tests on sensor perception within realistic, virtual environments, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with real-world testing.
Omniverse Cloud Sensor RTX microservices will be available later this year. Sign up for early access.
Showcasing Advanced AI With Research
Participants submitted research papers for the AI City Challenge and a few achieved top rankings, including:
- Overlap Suppression Clustering for Offline Multi-Camera People Tracking: This paper introduces a tracking method that includes identifying individuals within a single camera’s view, selecting clear images for easier recognition, grouping similar appearances, and helping to clarify identities in challenging situations.
- A Robust Online Multi-Camera People Tracking System With Geometric Consistency and State-aware Re-ID Correction: This research presents a new system that uses geometric and appearance data to improve tracking accuracy, and includes a mechanism that adjusts identification features to fix tracking errors.
- Cluster Self-Refinement for Enhanced Online Multi-Camera People Tracking: This research paper addresses specific challenges faced in online tracking, such as the storage of poor-quality data and errors in identity assignment.
All accepted papers will be presented at the AI City Challenge 2024 Workshop, taking place on June 17.
At CVPR 2024, NVIDIA Research will present over 50 papers, introducing generative physical AI breakthroughs with potential applications in areas like autonomous vehicle development and robotics.
Papers that used NVIDIA Omniverse to generate synthetic data or digital twins of environments for model simulation, testing and validation include:
- FoundationPose: Unified 6D Pose Estimation and Tracking of Novel Objects: FoundationPose is a versatile model for estimating and tracking the 3D position and orientation of objects. The model operates by using a few reference images or a 3D representation to accurately understand an object’s shape.
- Neural Implicit Representation for Building Digital Twins of Unknown Articulated Objects: This research paper presents a method for creating digital models of objects from two 3D scans, improving accuracy by analyzing how movable parts connect and move between positions.
- BEHAVIOR Vision Suite: Customizable Dataset Generation via Simulation: The BEHAVIOR Vision Suite generates customizable synthetic data for computer vision research, allowing researchers to adjust settings like lighting and object placement.
Read more about NVIDIA Research at CVPR, and learn more about the AI City Challenge.
Get started with NVIDIA Omniverse by downloading the standard license free, access OpenUSD resources and learn how Omniverse Enterprise can connect teams. Follow Omniverse on Instagram, Medium, LinkedIn and X. For more, join the Omniverse community on the forums, Discord server, Twitch and YouTube channels.
]]>NVIDIA today announced Nemotron-4 340B, a family of open models that developers can use to generate synthetic data for training large language models (LLMs) for commercial applications across healthcare, finance, manufacturing, retail and every other industry.
High-quality training data plays a critical role in the performance, accuracy and quality of responses from a custom LLM — but robust datasets can be prohibitively expensive and difficult to access.
Through a uniquely permissive open model license, Nemotron-4 340B gives developers a free, scalable way to generate synthetic data that can help build powerful LLMs.
The Nemotron-4 340B family includes base, instruct and reward models that form a pipeline to generate synthetic data used for training and refining LLMs. The models are optimized to work with NVIDIA NeMo, an open-source framework for end-to-end model training, including data curation, customization and evaluation. They’re also optimized for inference with the open-source NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM library.
Nemotron-4 340B can be downloaded now from the NVIDIA NGC catalog and from Hugging Face, where developers can also use the Train on DGX Cloud service to easily fine-tune open AI models. Developers will soon be able to access the models at ai.nvidia.com, where they’ll be packaged as an NVIDIA NIM microservice with a standard application programming interface that can be deployed anywhere.
Navigating Nemotron to Generate Synthetic Data
LLMs can help developers generate synthetic training data in scenarios where access to large, diverse labeled datasets is limited.
The Nemotron-4 340B Instruct model creates diverse synthetic data that mimics the characteristics of real-world data, helping improve data quality to increase the performance and robustness of custom LLMs across various domains.
Then, to boost the quality of the AI-generated data, developers can use the Nemotron-4 340B Reward model to filter for high-quality responses. Nemotron-4 340B Reward grades responses on five attributes: helpfulness, correctness, coherence, complexity and verbosity. It’s currently first place on the Hugging Face RewardBench leaderboard, created by AI2, for evaluating the capabilities, safety and pitfalls of reward models.
Researchers can also create their own instruct or reward models by customizing the Nemotron-4 340B Base model using their proprietary data, combined with the included HelpSteer2 dataset.
Fine-Tuning With NeMo, Optimizing for Inference With TensorRT-LLM
Using open-source NVIDIA NeMo and NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, developers can optimize the efficiency of their instruct and reward models to generate synthetic data and to score responses.
All Nemotron-4 340B models are optimized with TensorRT-LLM to take advantage of tensor parallelism, a type of model parallelism in which individual weight matrices are split across multiple GPUs and servers, enabling efficient inference at scale.
Nemotron-4 340B Base, trained on 9 trillion tokens, can be customized using the NeMo framework to adapt to specific use cases or domains. This fine-tuning process benefits from extensive pretraining data and yields more accurate outputs for specific downstream tasks.
A variety of customization methods are available through the NeMo framework, including supervised fine-tuning and parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods such as low-rank adaptation, or LoRA.
To boost model quality, developers can align their models with NeMo Aligner and datasets annotated by Nemotron-4 340B Reward. Alignment is a key step in training LLMs, where a model’s behavior is fine-tuned using algorithms like reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to ensure its outputs are safe, accurate, contextually appropriate and consistent with its intended goals.
Businesses seeking enterprise-grade support and security for production environments can also access NeMo and TensorRT-LLM through the cloud-native NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform, which provides accelerated and efficient runtimes for generative AI foundation models.
Evaluating Model Security and Getting Started
The Nemotron-4 340B Instruct model underwent extensive safety evaluation, including adversarial tests, and performed well across a wide range of risk indicators. Users should still perform careful evaluation of the model’s outputs to ensure the synthetically generated data is suitable, safe and accurate for their use case.
For more information on model security and safety evaluation, read the model card.
Download Nemotron-4 340B models via NVIDIA NGC and Hugging Face. For more details, read the research papers on the model and dataset.
See notice regarding software product information.
]]>Across industries, AI is supercharging innovation with machine-powered computation. In finance, bankers are using AI to detect fraud more quickly and keep accounts safe, telecommunications providers are improving networks to deliver superior service, scientists are developing novel treatments for rare diseases, utility companies are building cleaner, more reliable energy grids and automotive companies are making self-driving cars safer and more accessible.
The backbone of top AI use cases is data. Effective and precise AI models require training on extensive datasets. Enterprises seeking to harness the power of AI must establish a data pipeline that involves extracting data from diverse sources, transforming it into a consistent format and storing it efficiently.
Data scientists work to refine datasets through multiple experiments to fine-tune AI models for optimal performance in real-world applications. These applications, from voice assistants to personalized recommendation systems, require rapid processing of large data volumes to deliver real-time performance.
As AI models become more complex and begin to handle diverse data types such as text, audio, images, and video, the need for rapid data processing becomes more critical. Organizations that continue to rely on legacy CPU-based computing are struggling with hampered innovation and performance due to data bottlenecks, escalating data center costs, and insufficient computing capabilities.
Many businesses are turning to accelerated computing to integrate AI into their operations. This method leverages GPUs, specialized hardware, software, and parallel computing techniques to boost computing performance by as much as 150x and increase energy efficiency by up to 42x.
Leading companies across different sectors are using accelerated data processing to spearhead groundbreaking AI initiatives.
Finance Organizations Detect Fraud in a Fraction of a Second
Financial organizations face a significant challenge in detecting patterns of fraud due to the vast amount of transactional data that requires rapid analysis. Additionally, the scarcity of labeled data for actual instances of fraud poses a difficulty in training AI models. Conventional data science pipelines lack the required acceleration to handle the large data volumes associated with fraud detection. This leads to slower processing times that hinder real-time data analysis and fraud detection capabilities.
To overcome these challenges, American Express, which handles more than 8 billion transactions per year, uses accelerated computing to train and deploy long short-term memory (LSTM) models. These models excel in sequential analysis and detection of anomalies, and can adapt and learn from new data, making them ideal for combating fraud.
Leveraging parallel computing techniques on GPUs, American Express significantly speeds up the training of its LSTM models. GPUs also enable live models to process huge volumes of transactional data to make high-performance computations to detect fraud in real time.
The system operates within two milliseconds of latency to better protect customers and merchants, delivering a 50x improvement over a CPU-based configuration. By combining the accelerated LSTM deep neural network with its existing methods, American Express has improved fraud detection accuracy by up to 6% in specific segments.
Financial companies can also use accelerated computing to reduce data processing costs. Running data-heavy Spark3 workloads on NVIDIA GPUs, PayPal confirmed the potential to reduce cloud costs by up to 70% for big data processing and AI applications.
By processing data more efficiently, financial institutions can detect fraud in real time, enabling faster decision-making without disrupting transaction flow and minimizing the risk of financial loss.
Telcos Simplify Complex Routing Operations
Telecommunications providers generate immense amounts of data from various sources, including network devices, customer interactions, billing systems, and network performance and maintenance.
Managing national networks that handle hundreds of petabytes of data every day requires complex technician routing to ensure service delivery. To optimize technician dispatch, advanced routing engines perform trillions of computations, taking into account factors like weather, technician skills, customer requests and fleet distribution. Success in these operations depends on meticulous data preparation and sufficient computing power.
AT&T, which operates one of the nation’s largest field dispatch teams to service its customers, is enhancing data-heavy routing operations with NVIDIA cuOpt, which relies on heuristics, metaheuristics and optimizations to calculate complex vehicle routing problems.
In early trials, cuOpt delivered routing solutions in 10 seconds, achieving a 90% reduction in cloud costs and enabling technicians to complete more service calls daily. NVIDIA RAPIDS, a suite of software libraries that enables acceleration of data science and analytics pipelines, further accelerates cuOpt, allowing companies to integrate local search heuristics and metaheuristics like Tabu search for continuous route optimization.
AT&T is adopting NVIDIA RAPIDS Accelerator for Apache Spark to enhance the performance of Spark-based AI and data pipelines. This has helped the company boost operational efficiency on everything from training AI models to maintaining network quality to reducing customer churn and improving fraud detection. With RAPIDS Accelerator, AT&T is reducing its cloud computing spend for target workloads while enabling faster performance and reducing its carbon footprint.
Accelerated data pipelines and processing will be critical as telcos seek to improve operational efficiency while delivering the highest possible service quality.
Biomedical Researchers Condense Drug Discovery Timelines
As researchers utilize technology to study the roughly 25,000 genes in the human genome to understand their relationship with diseases, there has been an explosion of medical data and peer-reviewed research papers. Biomedical researchers rely on these papers to narrow down the field of study for novel treatments. However, conducting literature reviews of such a massive and expanding body of relevant research has become an impossible task.
AstraZeneca, a leading pharmaceutical company, developed a Biological Insights Knowledge Graph (BIKG) to aid scientists across the drug discovery process, from literature reviews to screen hit rating, target identification and more. This graph integrates public and internal databases with information from scientific literature, modeling between 10 million and 1 billion complex biological relationships.
BIKG has been effectively used for gene ranking, aiding scientists in hypothesizing high-potential targets for novel disease treatments. At NVIDIA GTC, the AstraZeneca team presented a project that successfully identified genes linked to resistance in lung cancer treatments.
To narrow down potential genes, data scientists and biological researchers collaborated to define the criteria and gene features ideal for targeting in treatment development. They trained a machine learning algorithm to search the BIKG databases for genes with the designated features mentioned in literature as treatable. Utilizing NVIDIA RAPIDS for faster computations, the team reduced the initial gene pool from 3,000 to just 40 target genes, a task that previously took months but now takes mere seconds.
By supplementing drug development with accelerated computing and AI, pharmaceutical companies and researchers can finally use the enormous troves of data building up in the medical field to develop novel drugs faster and more safely, ultimately having a life-saving impact.
Utility Companies Build the Future of Clean Energy
There’s been a significant push to shift to carbon-neutral energy sources in the energy sector. With the cost of harnessing renewable resources such as solar energy falling drastically over the last 10 years, the opportunity to make real progress toward a clean energy future has never been greater.
However, this shift toward integrating clean energy from wind farms, solar farms and home batteries has introduced new complexities in grid management. As energy infrastructure diversifies and two-way power flows must be accommodated, managing the grid has become more data-intensive. New smart grids are now required to handle high-voltage areas for vehicle charging. They must also manage the availability of distributed stored energy sources and adapt to variations in usage across the network.
Utilidata, a prominent grid-edge software company, has collaborated with NVIDIA to develop a distributed AI platform, Karman, for the grid edge using a custom NVIDIA Jetson Orin edge AI module. This custom chip and platform, embedded in electricity meters, transforms each meter into a data collection and control point, capable of handling thousands of data points per second.
Karman processes real-time, high-resolution data from meters at the network’s edge. This enables utility companies to gain detailed insights into grid conditions, predict usage and seamlessly integrate distributed energy resources in seconds, rather than minutes or hours. Additionally, with inference models on edge devices, network operators can anticipate and quickly identify line faults to predict potential outages and conduct preventative maintenance to increase grid reliability.
Through the integration of AI and accelerated data analytics, Karman helps utility providers transform existing infrastructure into efficient smart grids. This allows for tailored, localized electricity distribution to meet fluctuating demand patterns without extensive physical infrastructure upgrades, facilitating a more cost-effective modernization of the grid.
Automakers Enable Safer, More Accessible, Self-Driving Vehicles
As auto companies strive for full self-driving capabilities, vehicles must be able to detect objects and navigate in real time. This requires high-speed data processing tasks, including feeding live data from cameras, lidar, radar and GPS into AI models that make navigation decisions to keep roads safe.
The autonomous driving inference workflow is complex and includes multiple AI models along with necessary preprocessing and postprocessing steps. Traditionally, these steps were handled on the client side using CPUs. However, this can lead to significant bottlenecks in processing speeds, which is an unacceptable drawback for an application where fast processing equates to safety.
To enhance the efficiency of autonomous driving workflows, electric vehicle manufacturer NIO integrated NVIDIA Triton Inference Server into its inference pipeline. NVIDIA Triton is open-source, multi-framework, inference-serving software. By centralizing data processing tasks, NIO reduced latency by 6x in some core areas and increased overall data throughput by up to 5x.
NIO’s GPU-centric approach made it easier to update and deploy new AI models without the need to change anything on the vehicles themselves. Additionally, the company could use multiple AI models at the same time on the same set of images without having to send data back and forth over a network, which saved on data transfer costs and improved performance.
By using accelerated data processing, autonomous vehicle software developers ensure they can reach a high-performance standard to avoid traffic accidents, lower transportation costs and improve mobility for users.
Retailers Improve Demand Forecasting
In the fast-paced retail environment, the ability to process and analyze data quickly is critical to adjusting inventory levels, personalizing customer interactions and optimizing pricing strategies on the fly. The larger a retailer is and the more products it carries, the more complex and compute-intensive its data operations will be.
Walmart, the largest retailer in the world, turned to accelerated computing to significantly improve forecasting accuracy for 500 million item-by-store combinations across 4,500 stores.
As Walmart’s data science team built more robust machine learning algorithms to take on this mammoth forecasting challenge, the existing computing environment began to falter, with jobs failing to complete or generating inaccurate results. The company found that data scientists were having to remove features from algorithms just so they would run to completion.
To improve its forecasting operations, Walmart started using NVIDIA GPUs and RAPIDs. The company now uses a forecasting model with 350 data features to predict sales across all product categories. These features encompass sales data, promotional events, and external factors like weather conditions and major events like the Super Bowl, which influence demand.
Advanced models helped Walmart improve forecast accuracy from 94% to 97% while eliminating an estimated $100 million in fresh produce waste and reducing stockout and markdown scenarios. GPUs also ran models 100x faster with jobs complete in just four hours, an operation that would’ve taken several weeks in a CPU environment.
By shifting data-intensive operations to GPUs and accelerated computing, retailers can lower both their cost and their carbon footprint while delivering best-fit choices and lower prices to shoppers.
Public Sector Improves Disaster Preparedness
Drones and satellites capture huge amounts of aerial image data that public and private organizations use to predict weather patterns, track animal migrations and observe environmental changes. This data is invaluable for research and planning, enabling more informed decision-making in fields like agriculture, disaster management and efforts to combat climate change. However, the value of this imagery can be limited if it lacks specific location metadata.
A federal agency working with NVIDIA needed a way to automatically pinpoint the location of images missing geospatial metadata, which is essential for missions such as search and rescue, responding to natural disasters and monitoring the environment. However, identifying a small area within a larger region using an aerial image without metadata is extremely challenging, akin to locating a needle in a haystack. Algorithms designed to help with geolocation must address variations in image lighting and differences due to images being taken at various times, dates and angles.
To identify non-geotagged aerial images, NVIDIA, Booz Allen and the government agency collaborated on a solution that uses computer vision algorithms to extract information from image pixel data to scale the image similarity search problem.
When attempting to solve this problem, an NVIDIA solutions architect first used a Python-based application. Initially running on CPUs, processing took more than 24 hours. GPUs supercharged this to just minutes, performing thousands of data operations in parallel versus only a handful of operations on a CPU. By shifting the application code to CuPy, an open-sourced GPU-accelerated library, the application experienced a remarkable 1.8-million-x speedup, returning results in 67 microseconds.
With a solution that can process images and the data of large land masses in just minutes, organizations can gain access to the critical information needed to respond more quickly and effectively to emergencies and plan proactively, potentially saving lives and safeguarding the environment.
Accelerate AI Initiatives and Deliver Business Results
Companies using accelerated computing for data processing are advancing AI initiatives and positioning themselves to innovate and perform at higher levels than their peers.
Accelerated computing handles larger datasets more efficiently, enables faster model training and selection of optimal algorithms, and facilitates more precise results for live AI solutions.
Enterprises that use it can achieve superior price-performance ratios compared to traditional CPU-based systems and enhance their ability to deliver outstanding results and experiences to customers, employees and partners.
Learn how accelerated computing helps organizations achieve AI objectives and drive innovation.
]]>Taiwan’s leading consumer electronics giants are making advances with AI automation for manufacturing, as fleets of robots and millions of cameras and sensors drive efficiencies across the smart factories of the future.
Dozens of electronics manufacturing and automation specialists — including Foxconn, Pegatron and Wistron — are showcasing their use of the NVIDIA software at COMPUTEX, in Taipei, and are called out in NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang’s keynote address.
Companies displayed the latest in computer vision and generative AI using NVIDIA Metropolis for everything from automating product manufacturing to improving worker safety and device performance.
Creating Factory Autonomy
With increasing production challenges, manufacturers are seeing a need to turn factories into autonomous machines, with generative AI and digital twins as a foundation. AI agents — driven by large language models (LLMs) — are being built that can talk and assist on warehouse floors to boost productivity and increase safety. And digital twins are helping manufacturers simulate and develop factories and AI-powered automation before being deployed in real factories.
Foxconn and its Ingrasys subsidiary use NVIDIA Omniverse and Metropolis to build digital twins for factories, planning efficiency optimizations and worker safety improvement at a number of manufacturing sites. At COMPUTEX, Foxconn is showing how it uses digital twins to plan placements of many video cameras in factories to optimize its data capture for collecting key insights.
Bringing Generative AI to the Factory Floor
Generative AI is creating productivity leaps across industries. Researcher McKinsey forecasts that generative AI will deliver as much as $290 billion in value for the advanced manufacturing industry, while bringing $4.4 trillion annually to the global economy.
At GTC in March, NVIDIA launched NVIDIA NIM, a set of microservices designed to speed up generative AI deployment in enterprises. Supporting a wide range of AI models, it ensures seamless, scalable AI inferencing, on premises or in the cloud, using industry-standard application programming interfaces.
Billions of IoT devices worldwide can tap into Metropolis and NVIDIA NIM for improvements in AI perception to enhance their capabilities.
Advancing Manufacturing With NVIDIA NIM
Linker Vision, an AI vision insights specialist, is adopting NVIDIA NIM to assist factories in deploying AI agents that can respond to natural language queries.
The Taipei company uses NVIDIA Visual Insight Agent (VIA) in manufacturing environments for always-on video feed monitoring of factory floors. With user prompts, these ChatGPT-like systems can enable operators to ask for video of factory floors to be monitored for insights and safety alerts, like when workers are not wearing hardhats.
Operators can ask questions and receive instant, context-aware responses from AI agents, which can tap into organizational knowledge via retrieval-augmented generation, an integration of AI that can enhance operational efficiency.
Leading manufacturer Pegatron has factories that span more than 20 million square feet and the facilities process and build more than 15 million assemblies per month, while deploying more than 3,500 robots across factory floors. It has announced efforts based on NVIDIA NIM and is using Metropolis multi-camera tracking reference workflows to help with worker safety and productivity on factory lines. Pegatron’s workflow fuses digital twins in Omniverse and Metropolis real-time AI to better monitor and optimize operations.
Boosting Automated Visual Inspections
Adoption of NVIDIA Metropolis is helping Taiwan’s largest electronics manufacturers streamline operations and reduce cost as they build and inspect some of the world’s most complex and high-volume products.
Quality control with manual inspections in manufacturing is a multitrillion-dollar challenge. While automated optical inspection systems have been relied upon for some time, legacy AOI systems have high false detection rates, requiring costly secondary manual inspections for verification.
NVIDIA Metropolis for Factories offers a state-of-the-art AI reference workflow for bringing sophisticated and accurate AOI inspection applications to production faster.
TRI, Taiwan’s leading AOI equipment maker, has announced it’s integrating NVIDIA Metropolis for Factories workflow and capabilities into its latest AOI systems and is also planning to use NVIDIA NIM to further optimize system performance.
Wistron is expanding its OneAI platform for visual inspection and AOI with Metropolis. OneAI has been deployed in more than 10 Wistron factories globally, spanning hundreds of inspection points.
MediaTek, a leading innovator in connectivity and multimedia, and one of Taiwan’s largest IoT silicon vendors, announced at COMPUTEX that it’s teaming with NVIDIA to integrate NVIDIA TAO training and pretrained models into its AI development workflow for IoT device customers. The collaboration brings Metropolis and the latest advances in AI and visual perception to billions of IoT far-edge devices and streamlines software development for MediaTek’s next phase of growth in edge IoT.
Learn about NVIDIA Metropolis for Factories, NVIDIA NIM and the NVIDIA Metropolis multi-camera tracking workflow, which developers can use to build state-of-the-art real-time locating services and worker safety into their factory or warehouse operations.
]]>Basecamp Research is on a mission to capture the vastness of life on Earth at an unprecedented scale. Phil Lorenz, CTO at Basecamp Research, discusses using AI and biodiversity data to advance fields like medicine and environmental conservation with host Noah Kravitz in this AI Podcast episode recorded live at the NVIDIA GTC global AI conference. Lorenz explains Basecamp’s systematic collection of biodiversity data in partnership with nature parks worldwide and its use of deep learning to analyze and apply it for use cases such as protein structure prediction and gene editing. He also emphasizes the importance of ethical data governance and touches on technological advancements that will help drive the future of AI in biology.
Basecamp Research is a member of the NVIDIA Inception program for cutting-edge startups.
Stay tuned for more episodes recorded live at GTC, and hear more from Lorenz in this GTC session.
Time Stamps
1:31: What is Basecamp Research?
3:08: How does the process of sequencing biodiversity work?
5:15: What is the collected biodiversity data used for?
7:56: Gene editing and how biodiversity data can enhance it
9:00: How the development of AI has affected Basecamp’s work
14:33: Basecamp’s breakthroughs
16:49: AI and machine learning-related challenges Basecamp has encountered
26:02: Ethical considerations in data collecting
You Might Also Like…
AI2’s Christopher Bretherton Discusses Using Machine Learning for Climate Modeling – Ep. 220
Can machine learning help predict extreme weather events and climate change? Christopher Bretherton, senior director of climate modeling at the Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence, or AI2, explores the technology’s potential to enhance climate modeling.
Cardiac Clarity: Dr. Keith Channon Talks Revolutionizing Heart Health With AI – Ep. 212
Here’s some news to still beating hearts: AI is helping bring some clarity to cardiology. In this episode of NVIDIA’s AI Podcast, Dr. Keith Channon, cofounder and chief medical officer at the startup, speaks with host Noah Kravitz about Caristo, an AI-powered solution for detecting inflammation in cardiac CT scans.
Matice Founder Jessica Whited on Harnessing Regenerative Species for Medical Breakthroughs – Ep. 198
Scientists at Matice Biosciences are using AI to study the regeneration of tissues in animals known as super-regenerators, such as salamanders and planarians. The research aims to develop new treatments that will help humans heal from injuries without scarring.
Bojan Tunguz, Johnny Israeli on How AI and Crowdsourcing Can Advance Vaccine Distribution – Ep. 195
Artificial intelligence is teaming up with crowdsourcing to improve the thermo-stability of mRNA vaccines, making distribution more accessible worldwide. In this episode of NVIDIA’s AI podcast, host Noah Kravitz interviewed Bojan Tunguz, a physicist and senior system software engineer at NVIDIA, and Johnny Israeli, senior manager of AI and cloud software at NVIDIA, about AI’s potential in drug discovery.
Subscribe to the AI Podcast
Get the AI Podcast through iTunes, Google Podcasts, Google Play, Amazon Music, Castbox, DoggCatcher, Overcast, PlayerFM, Pocket Casts, Podbay, PodBean, PodCruncher, PodKicker, Soundcloud, Spotify, Stitcher and TuneIn.
Make the AI Podcast better: Have a few minutes to spare? Fill out this listener survey.
]]>